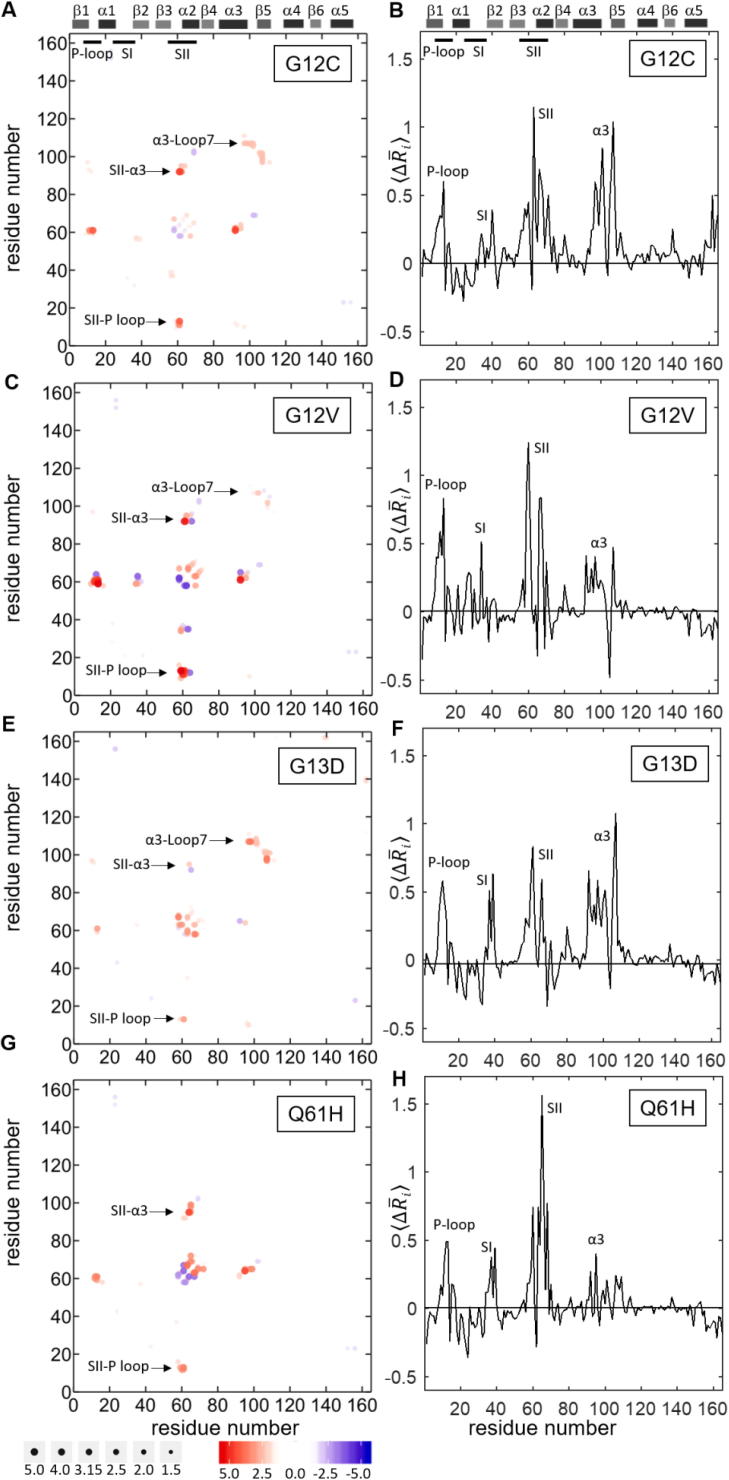
Fig. 2.
Alterations in active K-Ras conformations due to oncogenic mutations. Left panels: changes in pairwise residue distances (ij) in active K-Ras due to mutation. Positive ij values indicate divergent pairs (red); negative values indicate convergent pairs (blue). Right panels: all ij values averaged for each residue, (. Positive values indicate that the mutation causes a residue to move away from its neighbors; negative values indicate that a residue moves close to its neighbors. The predominant behavior for all studied mutants is positive (A-B) K-RasG12C (C-D) K-RasG12V (E-F) K-RasG13D (G-H) K-RasQ61H. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)