Fig. 2.
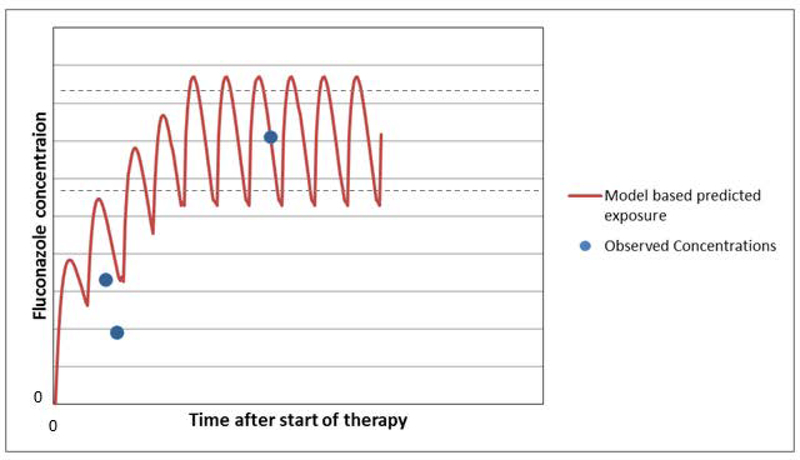
Using fluconazole treatment as an example in a two week infant born at 24 weeks gestation who is not on ECMO and has normal renal function the initial dosing regimen would suggest a loading dose of 25 mg/kg followed by a maintenance dose of 12 mg/kg every 12 hours. After fluconazole has been started a plasma drug level is obtained. Using the dosing information and drug level the 24 hour AUC can be calculated using the population PK model and compared to the goal (> 400 mg*hr/L). In this case the 24 hour AUC is too low. The decision support tool using Bayesian optimization then recommends a new dosing regimen so that the target AUC is obtained. The new dosing scheme with a higher maintenance dose every 12 hours after giving a one time loading dose is interrogated by obtaining another fluconazole level. The updated dosing regimen is subsequently simulated in the population PK model to determine the new 24 hour AUC. This time it is appropriate, thus the right dose has been determined for this patient