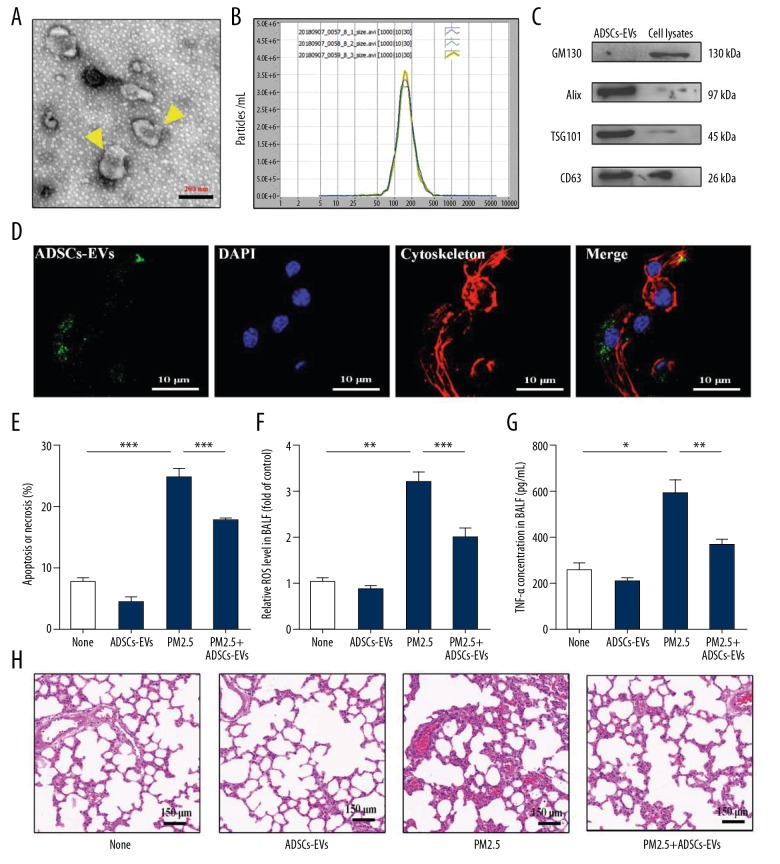
Figure 3.
ADSCs-EVs alleviated lung injury induced by PM2.5. (A) TEM identification of ADSCs-EVs. (B) NTA analysis of ADSCs-EVs. (C) GM130, Alix, TSG101, and CD63 expressions in ADSCs-EVs and cell lysates were detected by Western blotting. (D) The uptake of ADSCs-EVs in ATII cells was detected by a confocal microscopy. (E) Apoptosis or necrosis of ATII cells with treatments of PBS (None), ADSCs-EVs, PM2.5, or PM2.5+ADSCs-EVs was detected by flow cytometry assay. (F) Six hours after the rats treated with PBS (None), ADSCs-EVs, PM2.5 or PM2.5+ADSCs-EVs, relative ROS level in BALF was measured. (G) Six hours after the rats treated with PBS (None), ADSCs-EVs, PM2.5, or PM2.5+ADSCs-EVs, TNF-α concentration in BALF was evaluated. (H) HE staining of lungs exposed to PBS (None), ADSCs-EVs, PM2.5 or PM2.5+ADSCs-EVs. (* p<0.05; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001).