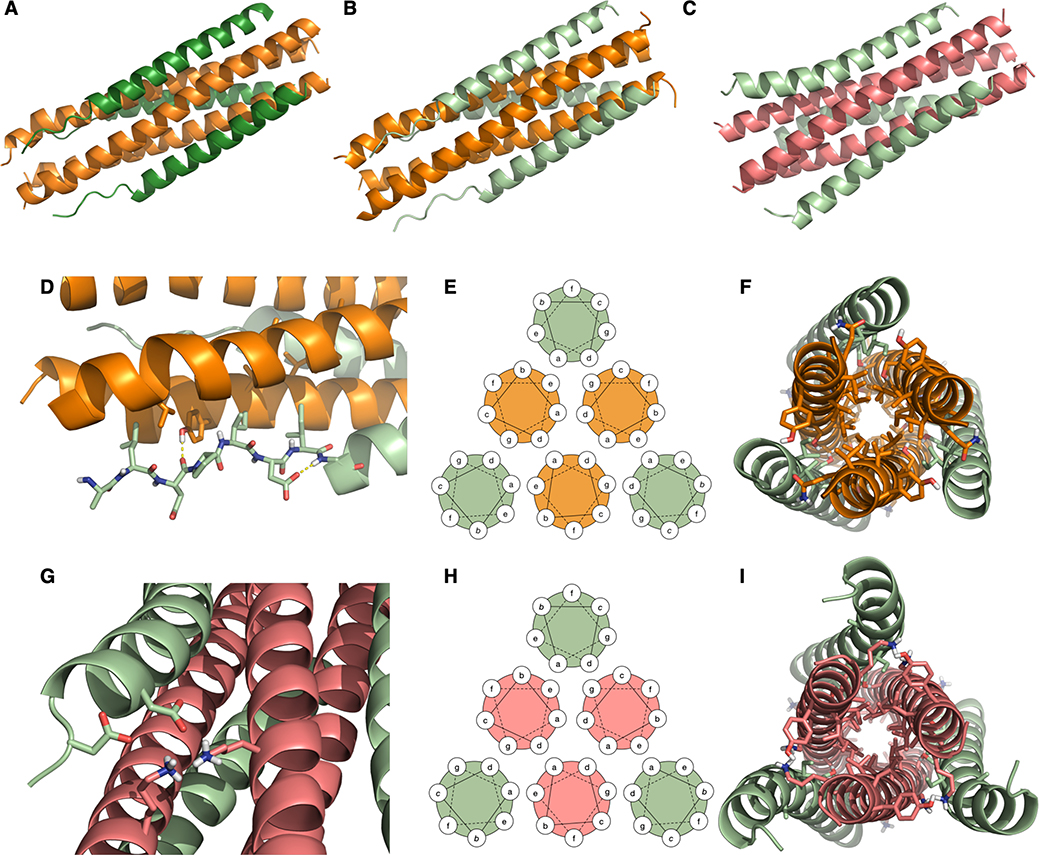
Figure 5.
Crystal structures of inhibitors bound to the HRN domains of HPIV3 and RSV F. (A) VI (dark green) + HPIV3 HRN (orange). (B) VIQKI (light green) + HPIV3 HRN (orange). (C) VIQKI (light green) + RSV HRN (salmon). (D) In the HPIV3 HRN+VIQKI co-assembly, the N-terminus of VIQKI adopts extended conformation with Leu451, Ile454, and Ile456 at the hydrophobic interface and Asp455 making an i,i+2 sidechain-to-backbone helix-capping interaction. (E) 6HB helical wheel diagram model. (F) Residues 457–484 follow the 6HB helical wheel model with a and d residues of the inhibitor interacting with a, d, e, and g residues of HPIV3 HRN. (G) In the RSV HRN+VIQKI co-assembly, the N-terminus of VIQKI adopts α-helical secondary structure with D452 and D455 engaged in salt bridge interactions with Lys191 and Lys196 of RSV HRN. (H) 6HB helical wheel diagram model. (I) Residues 463–484 follow 6HB helical wheel model with a and d residues of the inhibitor interacting with a, d, e, and g residues of RSV HRN.