Figure 2.
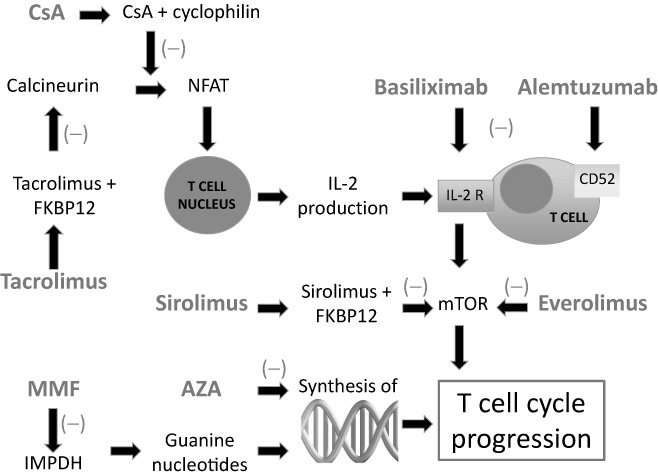
A schematic overview of the mechanisms of action of medications used for immunosuppression. IL‐2 is required for the activation of the mTOR pathway and progression of the T cell cycle. Both CsA and tacrolimus reduce the activation of NFAT, which in turn results in a decreased production of IL‐2. Basiliximab is a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the IL‐2 receptor. Sirolimus and everolimus inhibit the mTOR pathway through inhibition of specific enzymes. Alemtuzumab targets protein CD52 causing T cell dysfunction. Both MMF and AZA disrupt key elements of the deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis affecting the progression of the T cell cycle. AZA, azathioprine; Csa, cyclosporine A; FKBP12, FK‐binding protein 12; IMPDH,inosine‐50‐monophosphate dehydrogenase; IL‐2, interleukin‐2; IL‐2R, IL‐2 receptor; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T‐lymphocytes.
