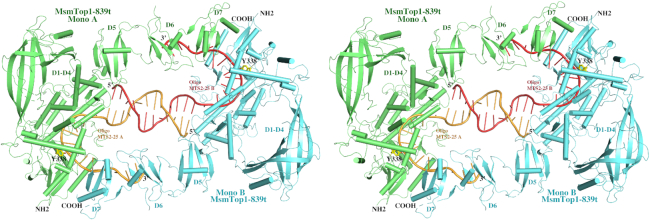
Figure 2.
A stereoview of a cartoon diagram of the overall structure of dimer-like MsmTOP1-839t in complex with oligonucleotide MTS2-25. The two MsmTOP1-839t monomers (Mono A and Mono B) are colored in green and cyan, respectively. Their bound MTS2-25 oligonucleotides (MTS2-25 A and MTS2-25 B) are colored in orange and salmon, respectively. The 5′-end regions of the two oligonucleotides primarily mediate the dimerization by forming a 12-base-pair duplex DNA containing six non-Watson–Crick base pairings and mismatches. The 3′-end of the oligonucleotide in one MsmTOP1-839t/MTS2-25 complex interacts with the D6-D7 domains of the other MsmTOP1-839t/MTS2-25 complex. As a result, the N-terminal and C-terminal domains of each MsmTOP1-839t are bound to two opposite strands of an underwound DNA duplex.