Figure 5.
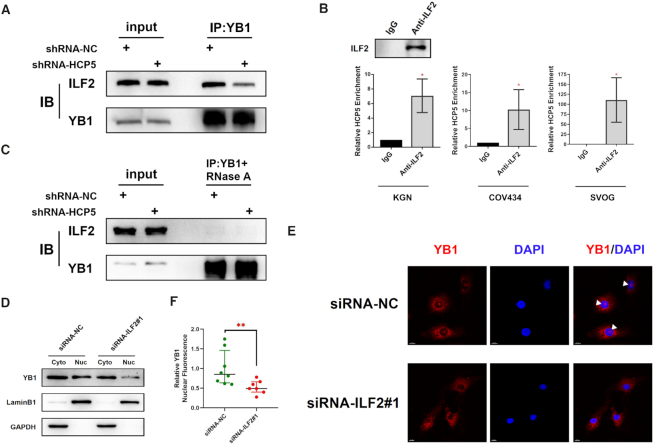
HCP5 is essential for YB1 locating to nucleus by acting as a scaffold for ILF2 and YB1. (A) The association between YB1 and ILF2 was shown in co-immunoprecipitation assays after silencing HCP5 in KGN cells. Data shown represent three independent experiments. (B) Confirmation of the interaction between ILF2 and HCP5 by RIP using ILF2 antibody in KGN, COV434 and SVOG cells. Results are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05. Two-tailed Student's t-test. (C) The association between YB1 and ILF2 was shown in co-immunoprecipitation assays after silencing HCP5 in KGN cells upon RNase A treatment. Data shown represent three independent experiments. (D) Subcellular localization of YB1 protein was detected by western blot after ILF2 silencing by siRNA in KGN cells. Lamin B1 was used as nuclear control. GAPDH was used as cytoplasmic control. (E) Subcellular localization of YB1 protein was confirmed by immunofluorescence assay after ILF2 silencing. White triangles indicate representative YB1 expression in the nucleus. (F) Quantification of nuclear immunofluorescence intensity (mean gray value) in ILF2-knockdown (n = 7) and negative control (n = 8) KGN cells. Data are presented as the median ± interquartile range. **P < 0.01. Two-tailed Mann–Whitney U-test.