Figure 2.
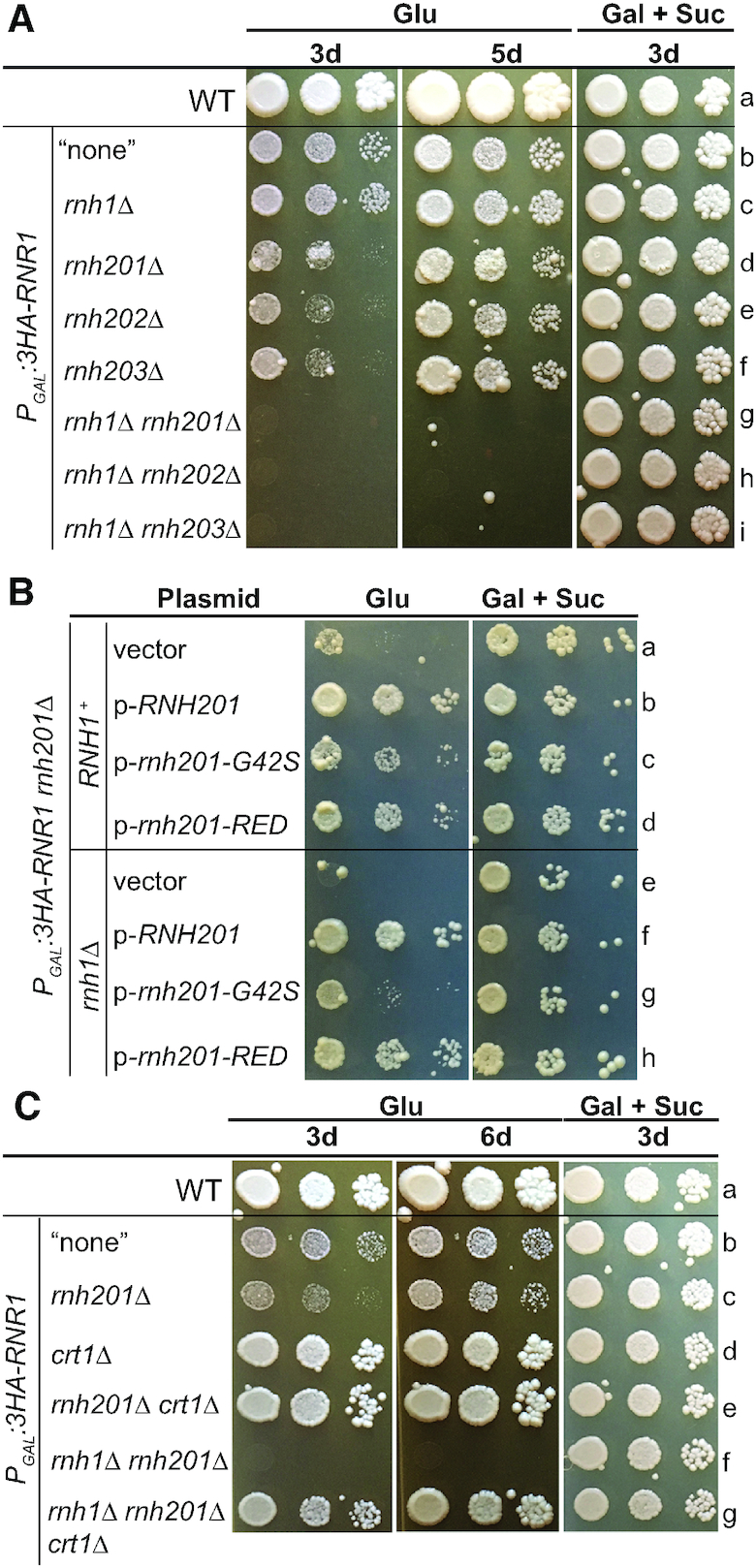
The lethality of Rnr1-depleted triple mutants lacking RNases H1 and H2 is suppressed by the variant Rnh201-RED. (A) Depletion of Rnr1 in mutants lacking RNase H1, RNase H2 or both enzymes has different effects on their growth. Drop test growth assays of strain WT, and strains carrying PGAL:3HA-RNR1 without gene deletion (labeled “none"), or with deletion of the gene RNH1, RNH201, RNH202, or RNH203, or both genes RNH1 and RNH201, or RNH1 and RNH202, or RNH1 and RNH203. Cells were grown in YPGS (2% galactose and 1% sucrose) liquid medium overnight at 30°C. Serial dilutions were plated on YEPD (2% glucose) and YPGS solid media. Plates were incubated at 30°C. Photographs were taken at the indicated number of days (d). ‘Glu’ stands for glucose. ‘Gal + Suc’ stands for galactose plus sucrose. The horizontal line across the images is included for clarity. See Supplementary Table S1 for the list of strains. For the ease of comparison, a unique Latin alphabet letter is allocated for each row. One representative experiment is shown of at least three independent ones. (B) The variant Rnh201-G42S suppresses less well the growth defects of Rnr1-depleted triple mutants lacking RNases H1 and H2 than the variant Rnh201-RED. Drop test growth assays of strains PGAL:3HA-RNR1 rnh201Δ and PGAL:3HA-RNR1 rnh201Δ rnh1Δ that have an empty vector, or a plasmid expressing WT Rnh201, variant Rnh201-G42S, or variant Rnh201-RED. Cells were grown overnight in liquid minimal medium lacking leucine with 2% galactose and 1% sucrose at 30°C. Serial dilutions were plated on solid minimal medium lacking leucine with either 2% glucose, or 2% galactose and 1% sucrose. Photographs were taken after 7 days of incubation at 30°C. For other details, see (A). (C) Cells depleted of Rnr1 and lacking RNases H1 and H2 grow like the WT strain in absence of Crt1. Drop test growth assays of strain WT, and strains carrying PGAL:3HA-RNR1 without gene deletion (labeled “none"), or with deletion of the gene RNH201 or CRT1, or both genes RNH201 and CRT1, or RNH1 and RNH201, or the three genes RNH1, RNH201 and CRT1. For other details, see (A).
