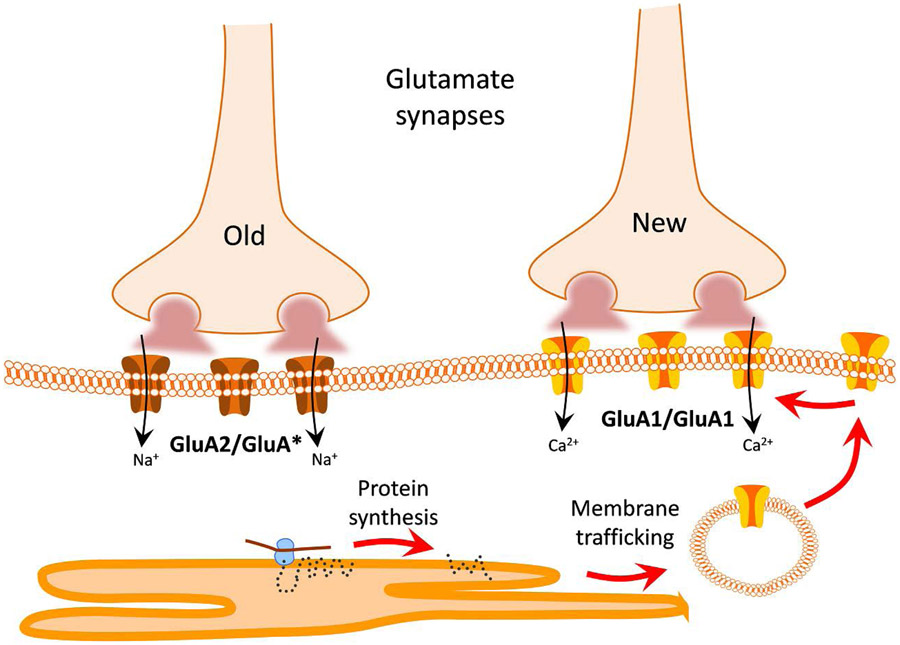
Figure 6. Model of AMPA receptor plasticity induced by salt loading.
New glutamate synapses formed during chronic salt loading are composed of Ca2+-permeable GluA1 homomeric AMPA receptors, which are highly labile, dependent on continuous protein synthesis for their maintenance and the maintenance of the new, but not the old, glutamate synapses. The old glutamate synapses are composed of GluA2-containing, Ca2+-impermeable AMPA receptors.