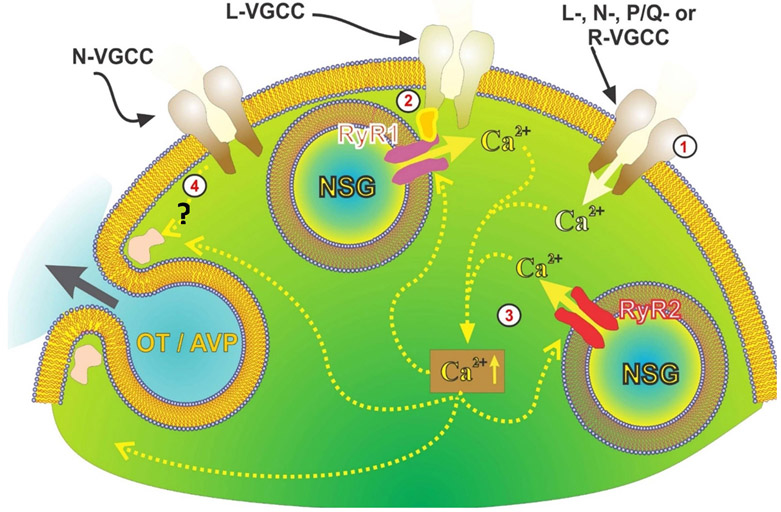
Figure 7. Model of different mechanisms of depolarization-induced neuropeptide secretion from OT/VP axon terminals.
1) Normally, secretion is activated by Ca2+ entry via different types of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (VGCC). 2) Independent of extracellular Ca2+, ryanodine type-1 receptors are activated in response to depolarization while mechanically tethered to nifedipine-sensitive Ca2+ channels. Depolarization, thus, allows for release of Ca2+ from ryanodine-sensitive stores contributing to the overall increase in intraterminal [Ca2+]. 3) This and Ca2+ entry through VGCCs likely contribute to CICR from ryanodine type-2 receptors. Intra-terminal free Ca2+ rise triggers the exocytosis releasing OT and arginine vasopressin (AVP). 4) Finally, there is secretion directly coupled to voltage and independent of both external and internal Ca2+. Drawing courtesy of Drs. Cristina Velazquez & Hector Marrero.