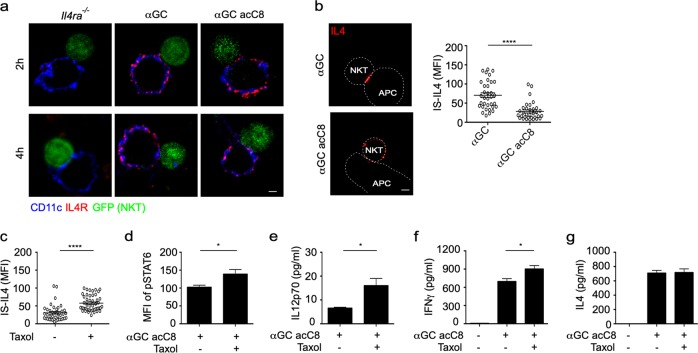
Fig. 5.
Taxol prolongs interleukin-4 (IL4) polarization in invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells and promotes α-galactosylceramide (αGC) acC8-induced T-helper type 1 (Th1) responses. a Distribution of IL4R (red) on the surface of CD11c+ (blue) dendritic cells (DCs). iNKT (GFP+) cells were activated by distinct antigen variant-pulsed splenic DCs for 4 h. Scale bars, 2 μm. Data are representative of two independent experiments and more than 25 cells per group. b Accumulation of IL4 at the immunological synapse (IS) in response to αGC-pulsed or αGC acC8-pulsed splenic DCs. Dotted lines indicate cell boundaries. Scale bars, 2 μm. Data are representative of three independent experiments (left) or are presented as the mean ± SEM of more than 35 cells per group (right). c Influence of taxol (100 nM) on the Th2 lipid-induced accumulation of IL4 at the IS, as shown in Fig. 4h. d–g Influences of taxol (100 nM) on the phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) in CD11c+ DCs (d) and on the production of IL12p70 (e), interferon-γ (IFNγ) (f), and IL4 (g) in the supernatant. iNKT cells were activated by αGC acC8-pulsed (1 μg/ml) DCs for 8 h. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using the Mann–Whitney U test. *P < 0.05 and ****P < 0.0001