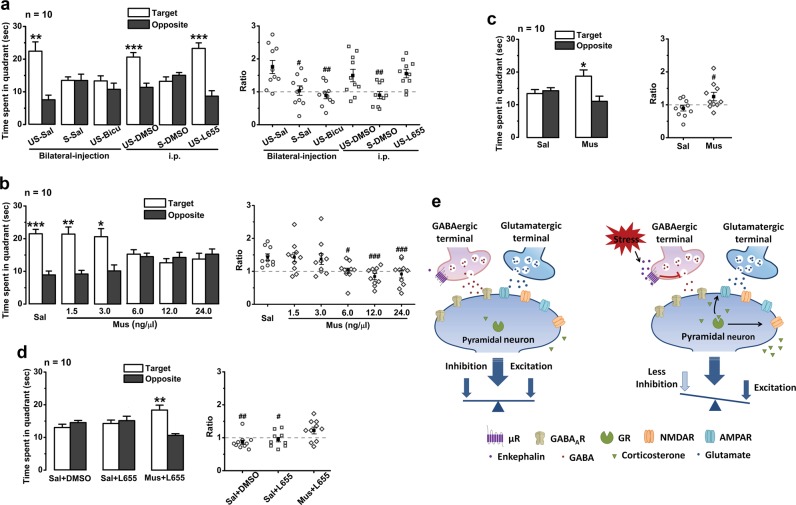
Fig. 5.
Intrasynaptic GABAA receptor-mediated inhibitory currents modulate memory retrieval. Symbol *, target vs. opposite within-group, paired Student’s t-test. a Memory retrieval of unstressed mice is damaged by application of bicuculline but not L-655,708 or vehicle before probe test. The target time ratio F5,54 = 6.37, p = 0.001, one-way ANOVA; #, vs. US-vehicle (saline or DMSO). b The effects of hippocampal infusion of different doses of muscimol on memory retrieval in unstressed mice. The target time ratio F5,54 = 6.34, p = 0.000, one-way ANOVA; #, vs. Sal. (c) Muscimol (1.5 ng/1.0 µl) infusion immediately after stress rescues the impaired memory retrieval. d Blocking tonic inhibitory currents with L-655,708 does not disturb the rescuing effect of muscimol on stress-impaired memory retrieval. The target time ratio F2,27 = 5.28, p = 0.012, one-way ANOVA; #, vs. Mus + L655. One symbol, p < 0.05; two symbols, p < 0.01; three symbols, p < 0.001. Sal saline, Bicu bicuculline, L655 L-655,708, Mus muscimol. e A schematic model for the two pathways in the hippocampus underlying the impairment of memory retrieval by acute stress. GR can directly modulate glutamatergic synaptic plasticity [4, 68] and affect memory retrieval. In addition, enkephalin triggered by acute stress in the hippocampus predominantly activates µRGABA and then disinhibits pyramidal neurons, resulting in E/I imbalance and impairment of memory retrieval