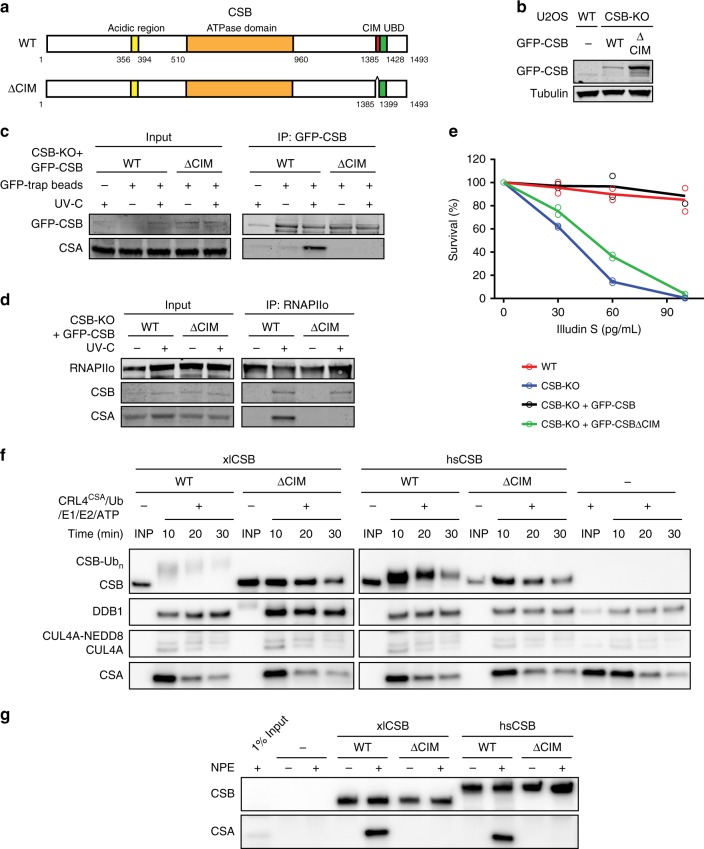
Fig. 3. The CIM of CSB mediates the recruitment of CSA to DNA damage-stalled RNAPIIo.
a A schematic representation of CSB and the CSBΔCIM mutant. b Western blot analysis of U2OS (FRT) and CSB-KO complemented with either GFP-CSBWT or GFP-CSBΔCIM (n = 2). c Co-IP of GFP-CSBWT and GFP-CSBΔCIM on the combined soluble and chromatin fraction. d Endogenous RNAPII Co-IP in GFP-CSBWT and GFP-CSBΔCIM cell lines. See also Supplementary Fig. 6e for additional Co-IP data. e Clonogenic Illudin S survival of WT and CSB-KO cell lines and the GFP-tagged CSB rescue cell lines. Each symbol represents the mean of an independent experiment (n = 2), each of which is based on two technical replicates. Note that the same survival data for WT, CSB-KO and CSB-KO + GFP-CSB is also shown in Fig. 1e. f In vitro ubiquitylation of recombinant Xenopus laevis (xl) and Homo sapiens (hs) CSB variants with recombinant xlCRL4CSA, E1, E2, ubiquitin, and ATP. At indicated times, in vitro ubiquitylation reactions were stopped and blotted with anti-FLAG (top three panels) or anti-xlCSA (bottom panel) antibodies. See also Supplementary Fig. 6d. g Immobilized recombinant CSB variants were incubated with Xenopus laevis nucleoplasmic extract (NPE), recovered, and blotted with anti-FLAG (top panel) or anti-xlCSA (bottom panel) antibody. At least two independent replicates of each IP and in vitro ubiquitylation experiment were performed obtaining similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.