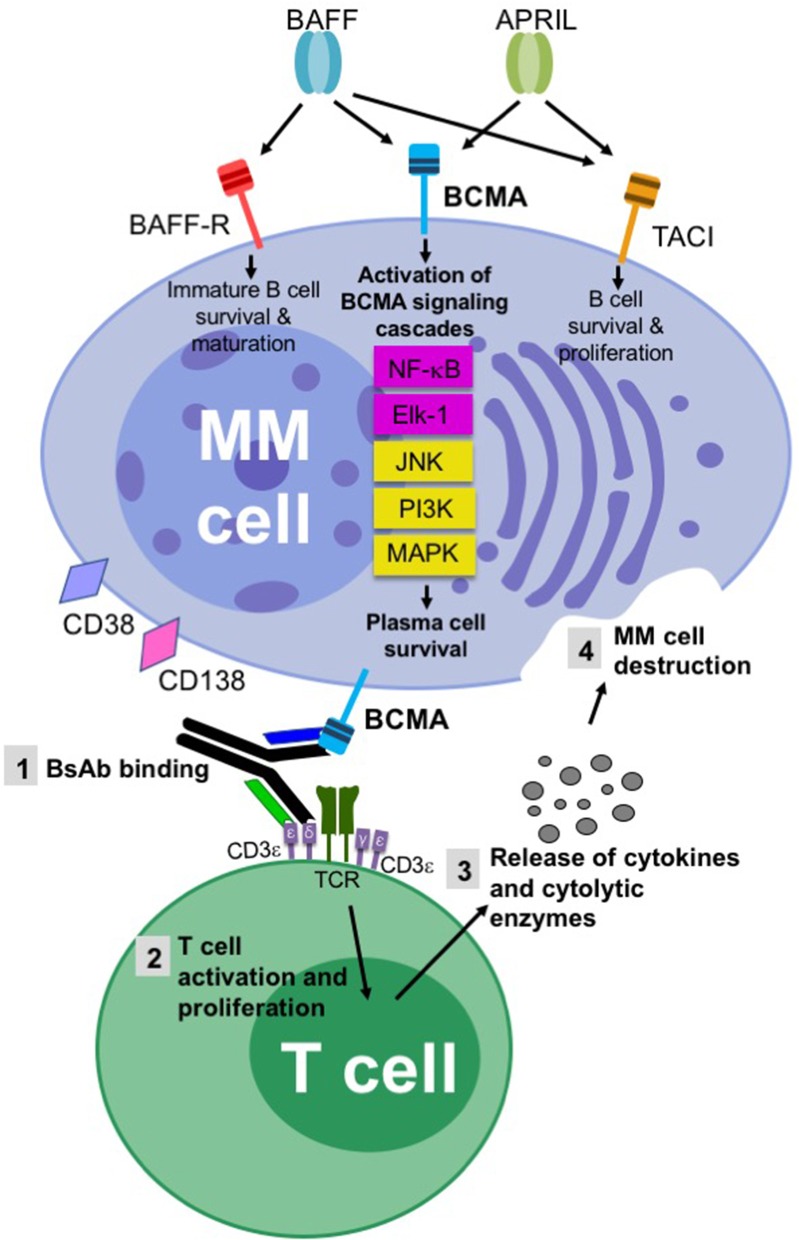
Figure 3.
Schematic of key tumor targets and the mechanism of action of BsAbs in multiple myeloma. The superior aspect of the figure highlights the importance of the BCMA/BAFF/APRIL axis and the associated BCMA signaling pathways for malignant plasma cell survival. The inferior aspect of the figure provides a schematic of how BsAbs induce effective T cell-directed MM cell death. A T cell redirecting BsAb binds to BCMA on a MM cell and CD3e on a T cell, coupling these two cells. NK cell redirecting BsAbs bind to CD16A rather than CD3e. Alternative BsAb targets on MM cells include CD38, CD138, FcLR5, CD19, CD319, GPRC5D, and NY-ESO-1. TCR-CD3e cross-linking leads to the activation and proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Cytokines (i.e., IFN-g, IL-2, IL-6, TNF-a) and cytolytic enzymes (i.e., granzyme B and perforin) are released, resulting in MM cell death.