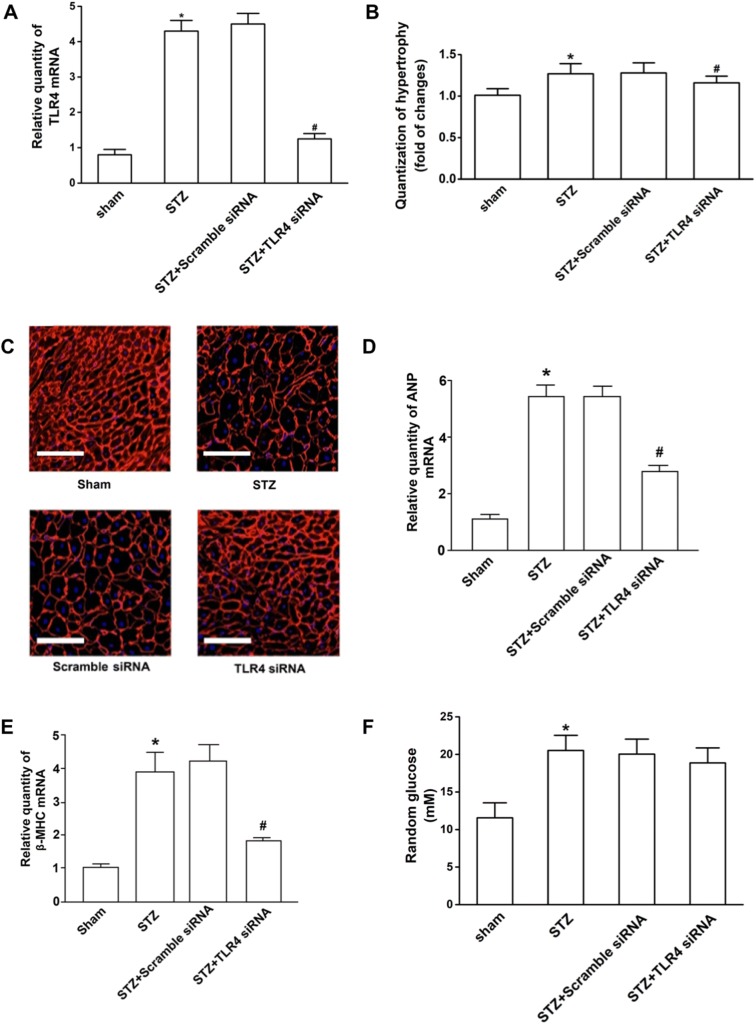
Fig. 1.
TLR4 siRNA displayed anti-hypertrophic effort in hearts of STZ-induced diabetic mice. Four experimental groups included the untreated mice (sham), diabetic mice (STZ), and the mice treated with scrambled siRNA and TLR4 siRNA. Each group contained ten mice. Eight weeks after treatment, hearts were excised, fixed, and sectioned. Total mRNA was extracted and used to detect the TLR4 transcripts by Q-RT-PCR. The relative quantity of TLR4 mRNA was expressed as mean ± SD. a TLR4 expression in the hearts of mice. TLR4 mRNA level was decreased by 72%, as compared with the mice treated with scrambled control siRNA after infusion of TLR4 siRNA. b Quantification of hypertrophic cells. To determine cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area, sections were stained with FITC-conjugated wheat germ agglutinin to detect membranes. Single cardiomyocytes in the sections were measured with a quantitative digital image analysis system. The outline of 200 cardiomyocytes was traced in each section. The increase of cell sizes was quantified as compared with the cardiomyocyte of normal mice (sham). c Representative fluorescence images of the hypertrophic cells (× 200). The scale bars are 50 μm. d, e Compared to the controls, the induction of cardiac fetal gene expression of ANP and β-MHC were reduced in TLR4 siRNA-treated hearts. f The levels of random glucose in TLR4 siRNA-treated mice with STZ-induced hyperglycemia were similar to those in the scrambled siRNA group (p > 0.05). #Statistical significance when compared with scrambled siRNA-treated mice, or * with untreated mice (sham) with STZ-induced mice were denoted as p < 0.05