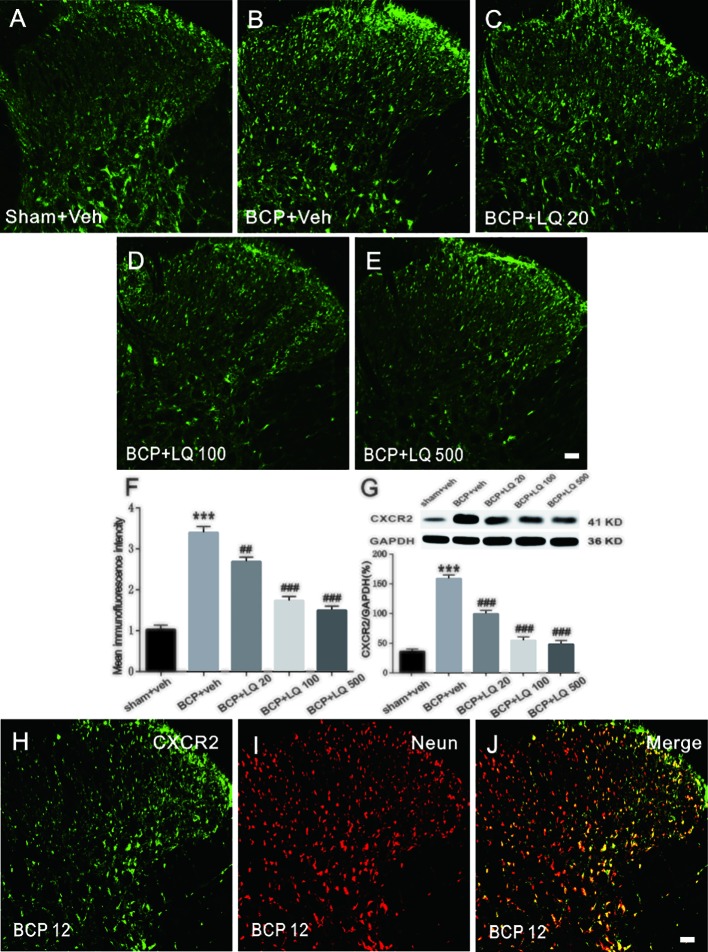
Figure 6.
Effects of intrathecal injection of Liquiritin (LQ) on bone cancer pain (BCP)-induced CXCR2 upregulation in the spinal neurons. (A–E) BCP induced a remarkable upregulation of CXCR2 in the ipsilateral spinal dorsal horn. Intrathecal LQ administration inhibited BCP-induced increase in CXCR2 immunoreactivity in the spinal cord. Scale bar 100 μm; mean immunofluorescence intensity (F) and western blot (G) of CXCR2 expressions after different treatments (F4,15 = 66.22, ***P < 0.001 vs. sham + Veh group; ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, vs. BCP + Veh group; F4,15 = 72.94, ***P < 0.001 vs. sham + Veh group; ###P < 0.001 vs. BCP + Veh group; n = 4, one way ANOVA, 6F, G). (H–J) Immunostaining images demonstrated CXCR2 (green) was predominantly co-localized with NeuN (red) as shown by overlapped staining (the rightmost panel, yellow). Scale bar, 100 μm.