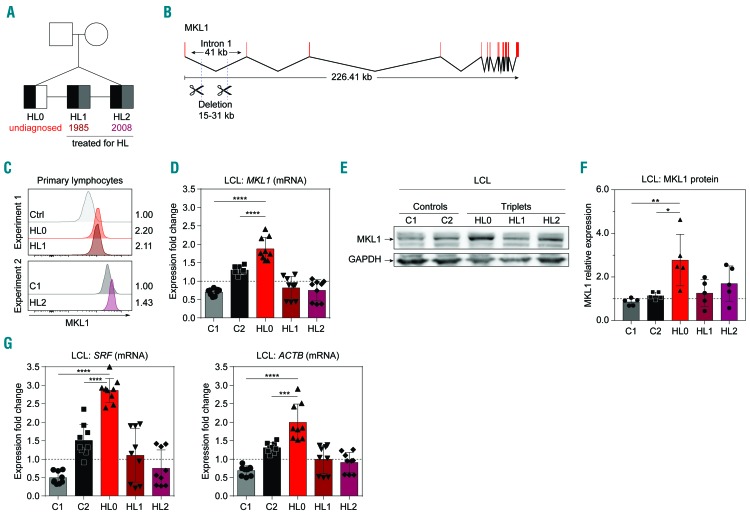
Figure 1.
The MKL1 intronic deletion is associated with increased expression of MKL1 and MKL1-induced genes. (A) Pedigree of genetically identical triplets (HL0, HL1, HL2) of whom two have been diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). Presence of the MKL1 intronic deletion is indicated in black, a diagnosis of HL in gray, and undiagnosed in white. Numbers indicate year of treatment. (B) Overview of MKL1 indicating the deletion in intron 1. (C) MKL1 protein expression in primary lymphocytes, determined by flow cytometry, in two separate experiments. Experiment 1: control (Ctrl), HL0, and HL1. Experiment 2: C1 and HL2. Numbers indicate the fold-change in expression normalized to the ctrl and C1 values, respectively. (D) MKL1 mRNA expression. (E) Representative image of MKL1 protein expression. (F) MKl1 expression normalized to GAPDH expression. (G) Expression of MKL1-induced genes by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. (D, F, G) Combined data from three experiments; experiments with primary lymphocytes (C) were performed once. For bar graphs, the dotted line indicates normalization to the mean of C1 and C2. All panels display data from lymphoblastoid cell lines except (C), which displays data from primary lymphocytes. Error bars represent the standard deviation of the measurements. Symbols represent technical replicates from three independent experiments in (D) and (G), and single values from independent experiments in (F). All data were analyzed using analysis of variance with a post-hoc Tukey test. ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.