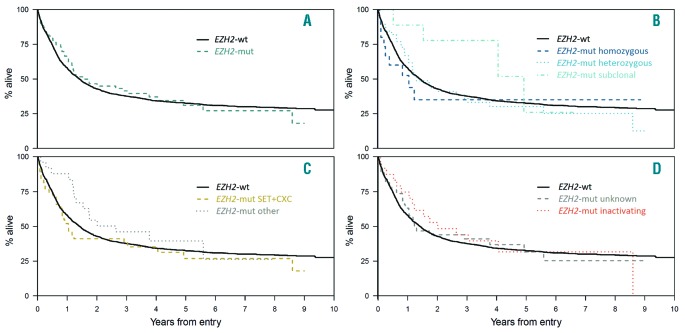
Figure 2.
Correlation of EZH2 mutational status with clinical outcome. Kaplan-Meier analysis showing overall survival of patients with (A) EZH2 -mutations (-mut) (n=63) versus wild type (–wt) (n=1,541) acute myeloid leukemia (B) homozygous (n=15) versus heterozygous (n=39) versus subclonal (n=9) EZH2 -mut (C) EZH2 mutations in affected functional (CXC-SET) (n=38) domains versus other EZH2 regions (n=25) and (D) EZH2 loss-of-function mutations (nonsense/frameshift) (n=24) versus missense mutations with unknown functional consequences (n=38).