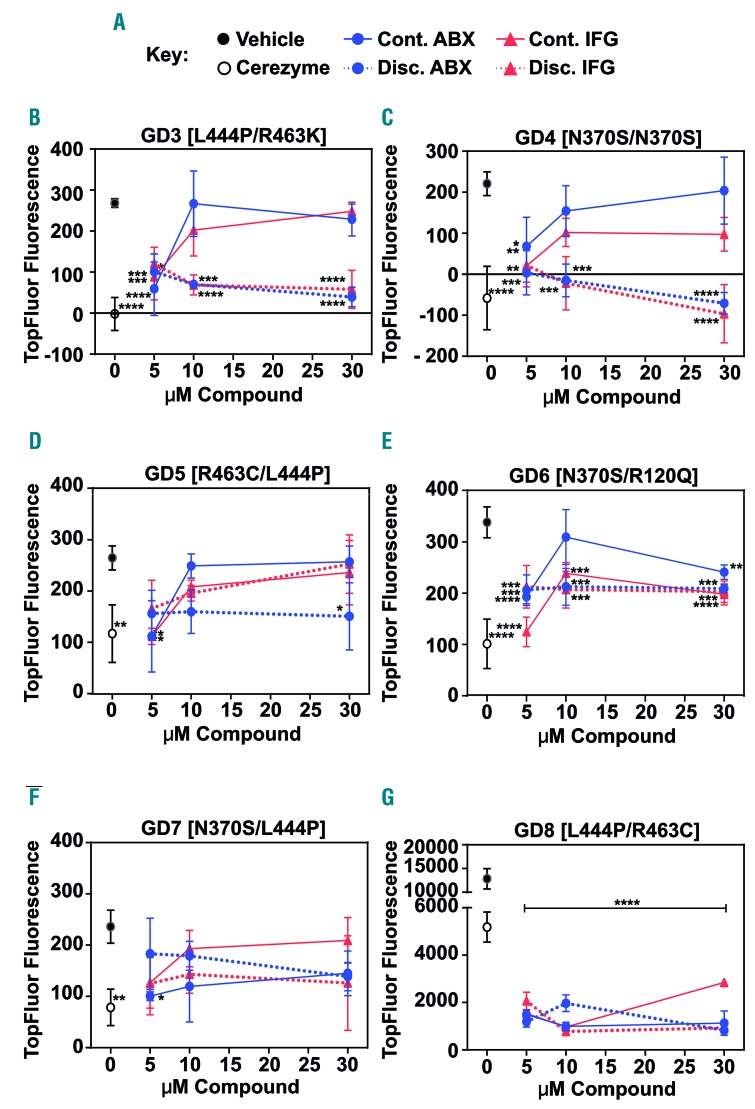
Figure 2.
Comparison of differential drug dosing protocols revealed a positive effect of glucocerebrosidase inhibitory chaperone compounds on lysosomal glucocerebrosidase function. Gaucher disease (GD) patient blood monocytic cell (PBMC)-derived macrophages were treated with 5, 10 or 30 μM ambroxol (ABX, blue) or isofagomine (IFG, red) or dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) vehicle control (black filled circles) either continuously (Cont.; solid lines) for 5 days or with discontinuation of treatment (Discont.; dashed lines) 24 h before the readout of TopFluor fluorescence (excitation at 485 nm and emission at 528 nm). Continuous treatment with 0.4 U Cerezyme (open circles) for 5 days was used as a control. (A) Key to compound treatment conditions (see Figure 1G for a schematic representation of the dosing schedules). (B-G) Quantification of TopFluor fluorescence in PBMC-derived macrophages from six different GD patients who harbored different combinations of GBA1 mutant alleles as shown. All samples were assayed in triplicate. Graphs show the mean and standard deviation. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance followed by the Dunnett test for multiple comparisons. *P≤0.05; **P≤0.01; ***P≤0.001, compared to the DMSO control.