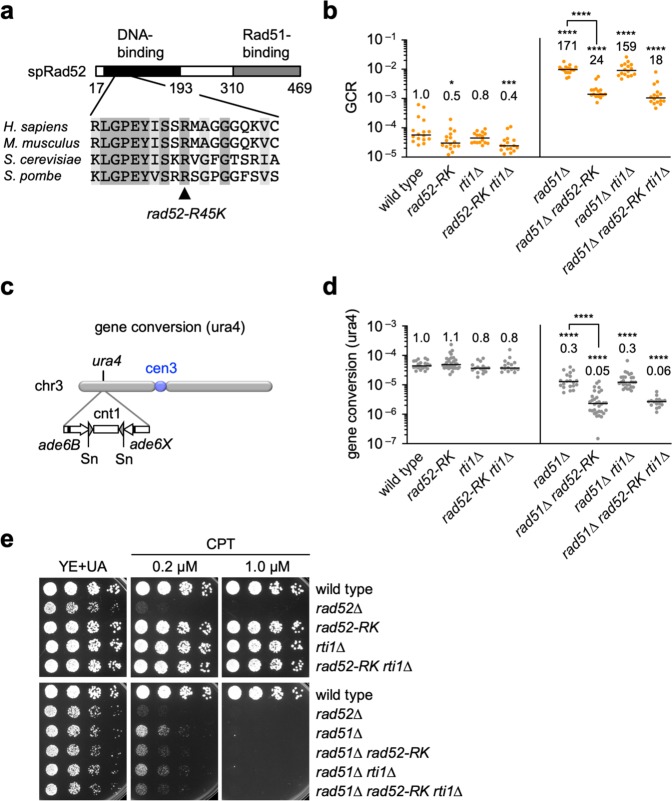
Fig. 3. The rad52-R45K mutation reduces GCRs.
a The rad52-R45K mutation site is located in the DNA-binding domain of Rad52. spRad52, S. pombe Rad52. b GCR rates of the wild-type, rad52-R45K, rti1∆, rad52-R45K rti1∆, rad51∆, rad51∆ rad52-R45K, rad51∆ rti1∆, and rad51∆ rad52-R45K rti1∆ strains (TNF5369, 6599, 6707, 7879, 5411, 6616, 6725, and 7886, respectively). c The ade6B and ade6X repeats integrated at the ura4 locus of chr3 are illustrated26. Sn, SnaBI. d Gene conversion rates at the ura4 locus in the wild-type, rad52-R45K, rti1∆, rad52-R45K rti1∆, rad51∆, rad51∆ rad52-R45K, rad51∆ rti1∆, and rad51∆ rad52-R45K rti1∆ strains (TNF3631, 5995, 5389, 7878, 3635, 6021, 5427, and 7890, respectively). *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; ns, non-significant P > 0.05. e Exponentially growing cells of the strains in d and the rad52∆ (TNF3643) strain were 5-fold serially diluted in water and spotted onto YE + UA plates supplemented with CPT. Source data for the graphs in b, d are available in Supplementary Data 1.