Fig. 7. DNA Pol α and Swi1 prevent Rad52-dependent GCRs at centromeres.
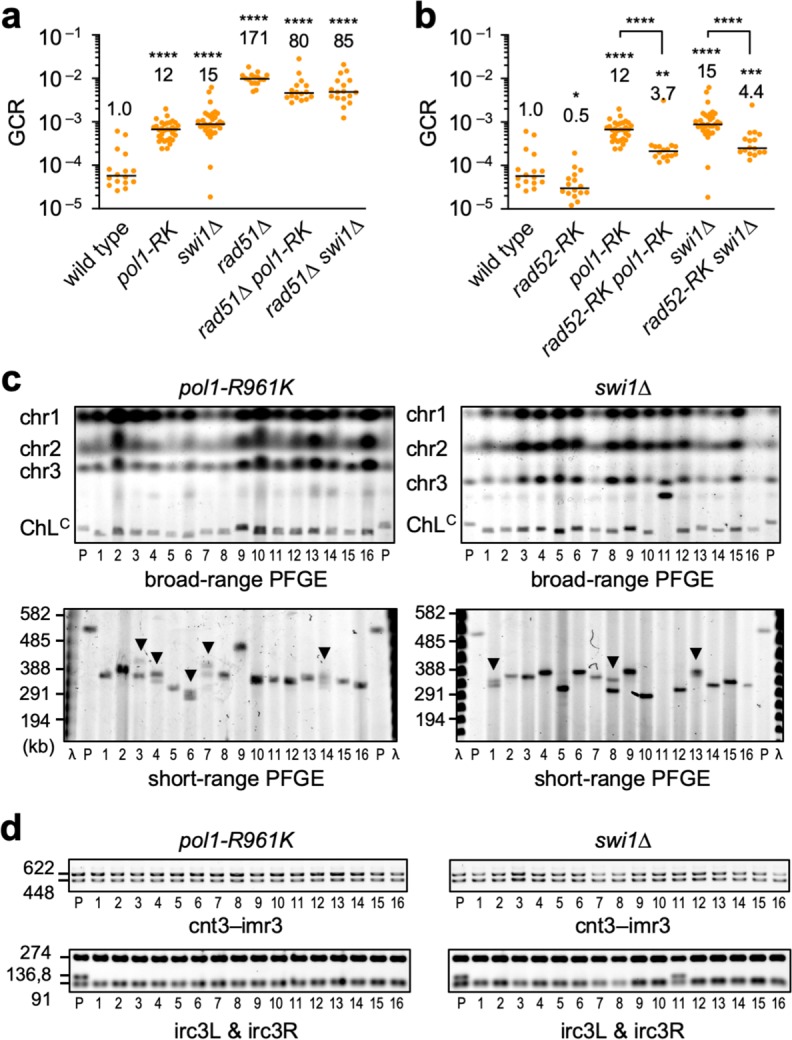
a GCR rates of the wild-type, pol1-R961K, swi1∆, rad51∆, rad51∆ pol1-RK, and rad51∆ swi1∆ strains (TNF5369, 6678, 6952, 5411, 6833, and 7909, respectively). b GCR rates of the wild-type, rad52-R45K (TNF6599), pol1-R961K, rad52-R45K pol1-R961K (TNF6695), swi1∆, and rad52-R45K swi1∆ (TNF6954) strains. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. c Chromosomal DNAs from parental strains and independent GCR clones of pol1-R961K and swi1∆ were separated by broad- and short-range PFGE and stained with EtBr, as shown in Fig. 2b. Arrowheads indicate samples containing GCR products of different sizes. d PCR analysis of GCR products. Both sides of the cnt3–imr3 junctions (cnt3–imr3) and outermost repeats (irc3L & irc3R) were examined. Uncropped images of the gels presented in c, d are shown in Supplementary Fig. 9. Source data used for the graphs in a, b are available in Supplementary Data 1.
