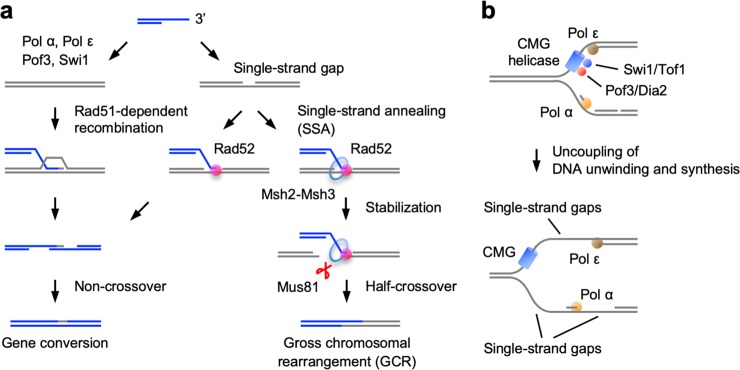
Fig. 8. The replication machinery promotes Rad51-dependent recombination and prevents Rad52-dependent SSA at centromeres.
a The replication machinery containing Pol α, Pol ε, Pof3, and Swi1 promotes Rad51-dependent recombination by preventing single-strand gap formation at centromeres (left). However, when single-strand gaps are formed on the template DNA, Rad52-dependent SSA occurs between a pair of complementary ssDNAs (right). Specific involvement of Msh2, Msh3, and Mus81 in Rad52-dependent GCRs suggests that joint molecules formed by Rad52-dependent SSA are stabilised by the Msh2–Msh3 ring-like complex, and are resolved by the Mus81 endonuclease into half-crossover products. Half-crossover between inverted repeats that are present on the opposite sides of sister centromeres results in the formation of isochromosomes. Dissociation of the joint molecule that occurs independently of Msh2–Msh3 and Mus81 may result in gene conversion through non-crossover recombination. b The CMG helicase, which consists of Cdc45, MCM2-7, and GINS, is involved in the progression of replication forks. Swi1/Tof1 and Pof3/Dia2, which are associated with the CMG helicase, and lagging- and leading-strand polymerases (Pol α and Pol ε, respectively) are required for tight coupling of DNA unwinding and synthesis at centromeres. Mutations in these replication proteins can uncouple DNA unwinding and synthesis, resulting in the formation of single-strand gaps, which in turn can be used in Rad52-dependent SSA.