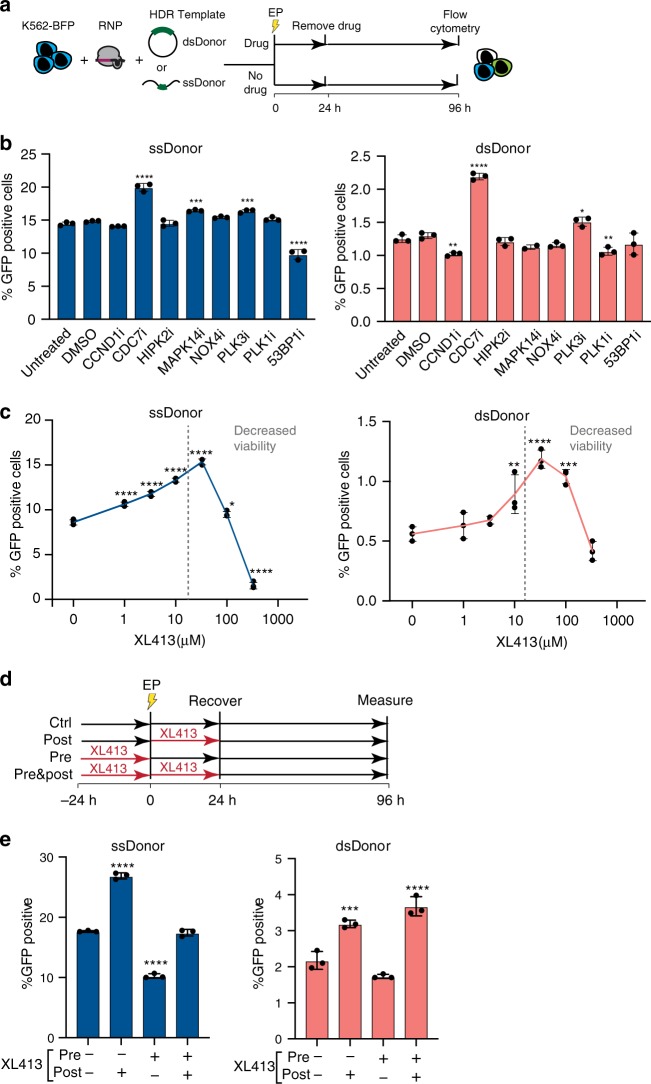
Fig. 2. Enhancing HDR by small molecule inhibition of factors discovered in genetic screening.
a Schematic of small molecule evaluation. K562-BFP cells were nucleofected with Cas9-RNPs targeting the BFP transgene and either plasmid dsDonor or oligonucleotide ssDonor templates. After electroporation (EP), cells were added to media with or without compound. Cell populations were recovered into fresh media after 24 h and analyzed by flow cytometry after 96 h. b CDC7 inhibition with XL413 significantly increases SSTR and HR. Shown is the percentage of GFP-positive cells by flow cytometric analysis of K562-BFP cell populations 4 days post nucleofection with ssDonor (left) or dsDonor (right) comparing different chemical compound treatments. X-axis indicates the intended molecular target of the small molecule inhibitors. c XL413 increases HDR in a concentration-dependent manner for both SSTR and HR pathways. Shown is the percentage of GFP positive cells 4 days post nucleofection for editing with ssDonor (left) and plasmid dsDonor (right). Dashed line indicates point where XL413 toxicity becomes significant. d Schematic showing strategies for pre-treatment and post-treatment with XL413. e Editing outcomes in K562-BFP depend on timing of XL413 administration. Cells were untreated, treated for 24 h with XL413 before nucleofection (pre), treated for 24 h with XL413 after nucleofection (post) or both (pre- and post). Percentage of GFP positive cells was determined 4 days post nucleofection using flow cytometry. All values are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3 biological replicates). Statistical significances were calculated by ordinary one-way ANOVA and Dunnet’s multiple comparison test comparing different treatments to the control (adjusted p-values are reported as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001). Source data are available in the Source Data file.