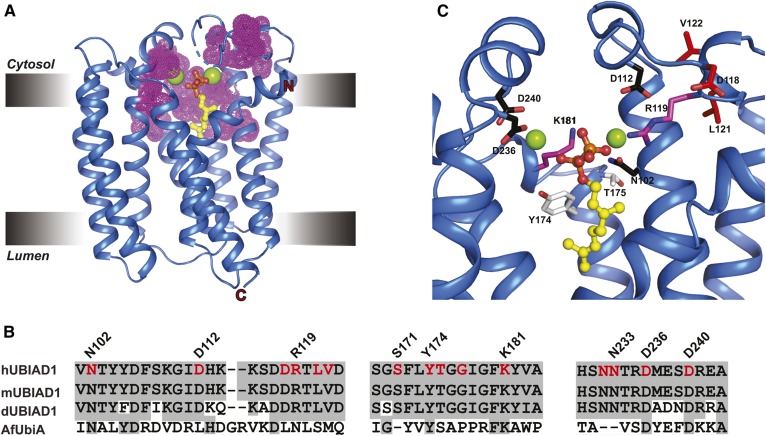
Fig. 6.
SCD-associated mutations cluster around the substrate-binding and catalytic active site of human UBIAD1. A: Structure of a UbiA homolog from Archaeoglobus fulgidus (AfUbiA) bound to Gpp and Mg2+. Residues corresponding to SCD-associated mutations in human UBIAD1 are indicated by magenta dots. B: Amino acid sequence alignment of conserved motifs in human, mouse, Drosophila UBIAD1 (hUBIAD1, mUBIAD1, and dUBIAD1, respectively), and AfUbiA. Conserved residues are shaded in gray and SCD-associated mutations are indicated and highlighted in red. C: Zoomed view of human UBIAD1 catalytic active site model built by PyMOL using AfUbiA as a template. The side chains (stick) of residues mutated in SCD are as follows: coordination of Mg2+ ion (black), coordination of isoprenyl phosphate group (magenta), positioned in putative catalytic lid (magenta), and active site residues (white).