Fig. 11.
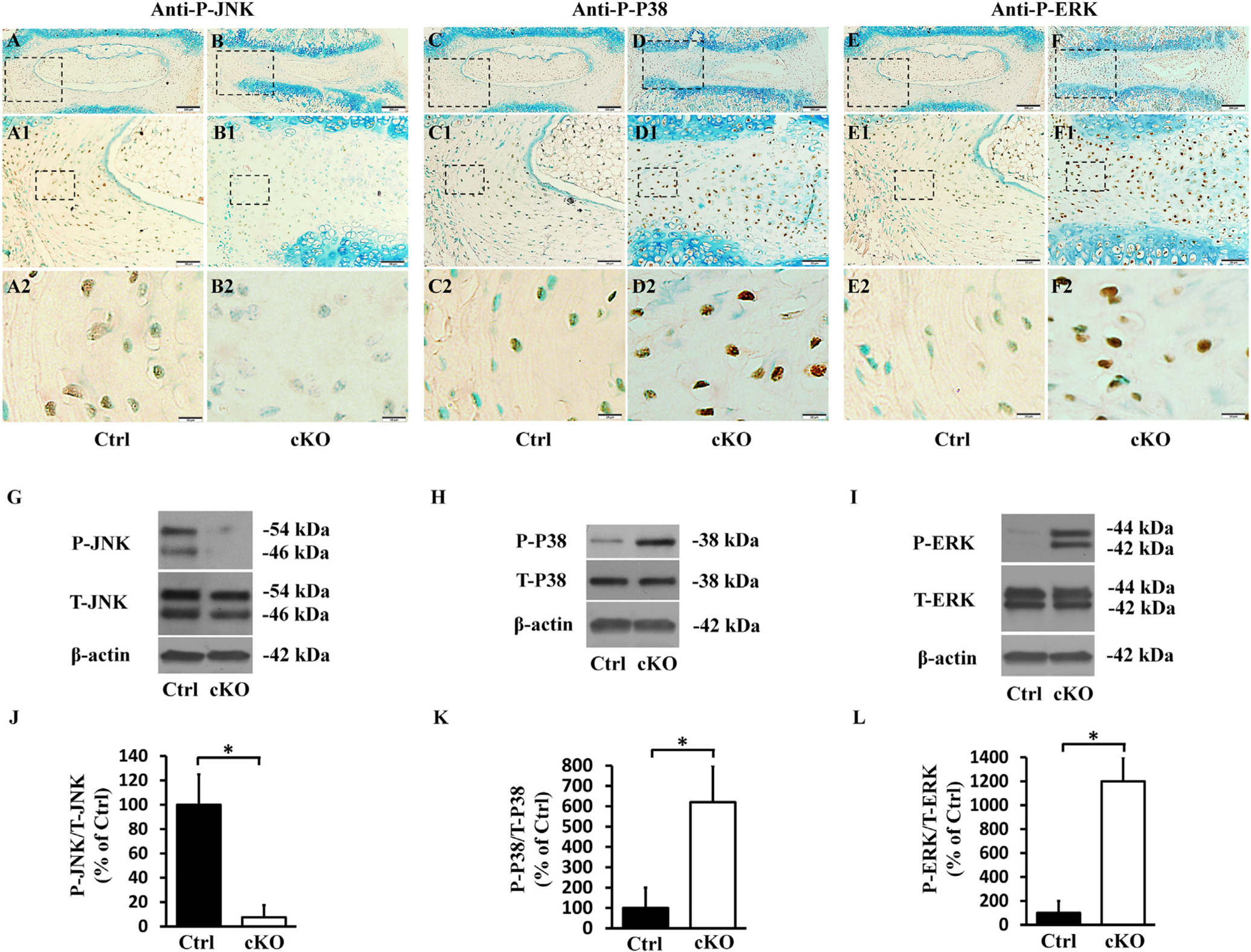
Inactivation of FAM20B altered the levels of molecules in MAPK signaling pathway in AF. (A, B, C, D, E, F) IHC analyses of P-JNK, PeP38 and P-ERK in the IVDs of 3-week-old control and cKO mice (representative images of at least 3 mice for each group). A1, B1, C1, D1, E1, F1 were the higher magnification views of the black boxes in A, B, C, D, E, F, respectively. A2, B2, C2, D2, E2, F2 were the higher magnification views of the black boxes in A1, B1, C1, D1, E1, F1, respectively. The numbers of P-JNK positive cells were reduced in the AF of cKO mice, while the numbers of PeP38 and P-ERK positive cells were significantly increased in the AF of cKO mice (Bars in the A, B, C, D, E, F = 200 μm, Bars in the A1, B1, C1, D1, E1, F1 = 50 μm, Bars in the A2, B2, C2, D2, E2, F2 = 10 μm). (G, H, I) Protein levels of P-JNK, PeP38 and P-ERK in the AF of 3-week-old mice as detected by Western immunoblotting. (J, K, L) Relative levels of P-JNK, PeP38 and P-ERK to total JNK, P38 and ERK illustrated in Western immunoblotting analyses. The protein level of P-JNK was lower while those of PeP38 and P-ERK were significantly higher in AF of cKO mice than in the control (n = 3, * = p < 0.05).
