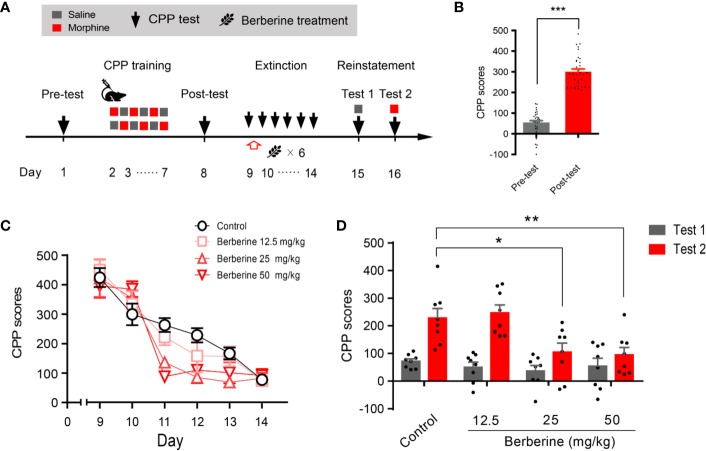
Figure 1.
The effect of berberine on extinction of morphine-induced drug-associated behavior in free access CPP extinction paradigm (A) The experimental timeline of behavioral training and tests, and drug treatments (B) CPP scores of pre-test and post-test, which were conducted before and after CPP training. Significant place preference was observed after morphine-paired CPP training. n = 32; ***p < 0.001, compared to the pre-test (C) Extinction of morphine-induced drug-associated behavior in a free access CPP extinction paradigm. Corn oil (1 mL/kg, i.g.) and berberine (12.5, 25, and 50 mg/kg, i.g.) were administered to mice in the control and berberine treatment groups, respectively, 1 h after each extinction training session (D) Reinstatement of morphine-induced CPP. A priming injection of saline (1 mL/kg, i.p.) and morphine (3 mg/kg, i.p.) was administered 10 min before the reinstatement tests 1 and 2, respectively. n = 8 for each group; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, compared to the control group. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. CPP, conditioned place preference.