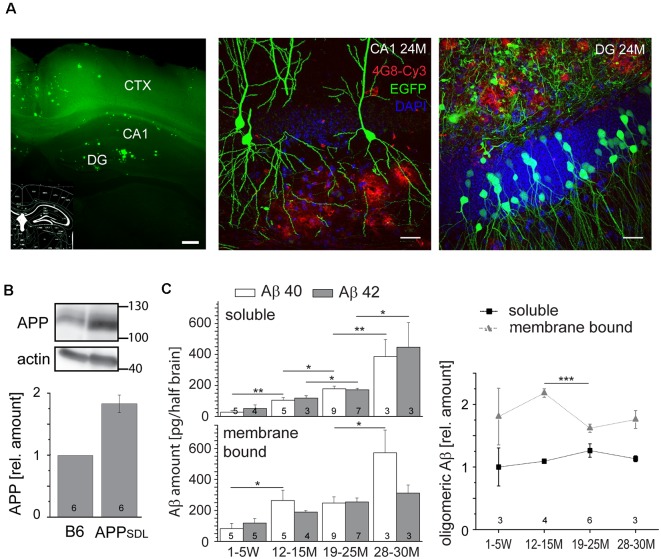
Figure 1.
Amyloid beta (Aβ) precursor protein (APPSDL) mice accumulate Aβ40/Aβ42 during life with relatively stable amounts of the oligomeric forms. (A) Thioflavin S staining of a coronal vibratome section from a 24-month-old APPSDL mouse, left. Confocal laser scanning micrographs showing Aβ deposits (4G8 staining, red) in the hippocampus from coronal sections of APPSDL mice expressing EGFP in a population of hippocampal pyramidal neurons within the CA1 subfield, middle, and granule cells within the dentate gyrus (DG), right. Cell nuclei were visualized using DAPI. (B) The expression level of APP in B6 and APPSDL animals. Immunoblot (top) of forebrain lysates from 24 months old mice detected with an anti-APP antibody that recognizes both human and mouse APP. Staining against actin is shown as loading control. Quantitation (bottom) of the APP signal was performed relative to actin and the value for B6 animals was set as 1.0. (C) Amount of soluble and membrane-bound human Aβ40 and Aβ42 (left), and the relative amount of oligomeric Aβ (right) from APPSDL animals of different ages. Quantitation was performed by ELISA after the sequential extraction of brain lysates. The number of mice for each condition is indicated in bars (left) or right above the x-axis (right). Data represent mean ± SEM; the number of mice per genotype is shown at the graphs. Data were analyzed using Student’s t-tests to address potential alterations between adjacent time points within the same condition and considered to be significantly different at *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001. Scale bar, 200 μm (A) left, 20 μm (A) middle, right.