Figure 1.
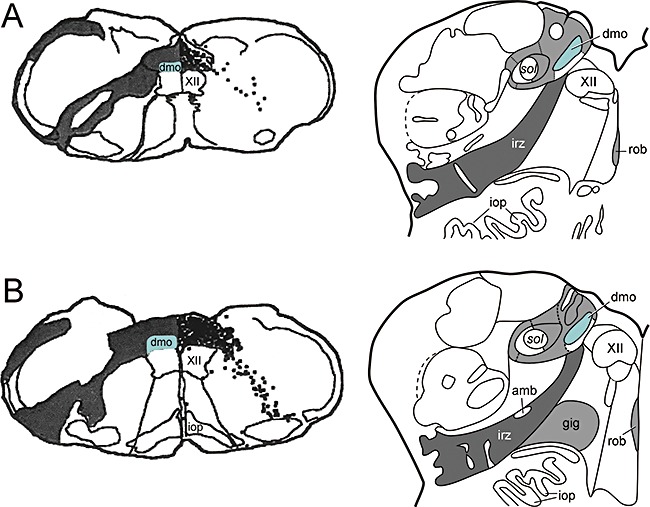
(A–B, left hand side) to illustrate the mode of spread of herpes simplex virus following injection into peripheral portions of the vagus nerve in the rat medulla oblongata, adapted and reproduced in part with permission from Blessing et al.[154]. (A–B, right hand side) to show the topographical distribution pattern of α‐synuclein pathology in the human medulla in stages 1 and 2 of sporadic Parkinson's disease, adapted and reproduced in part with permission from Del Tredici et al.[21]. amb, ambiguus nucleus; dmo, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (marked in green); gig, gigantocellular reticular nucleus, iop, inferior olivary nucleus, principal subnucleus; irz, intermediate reticular zone; rob, nucleus raphes obscurus; sol, solitary tract; XII, motor nucleus of the hypoglossal nerve.
