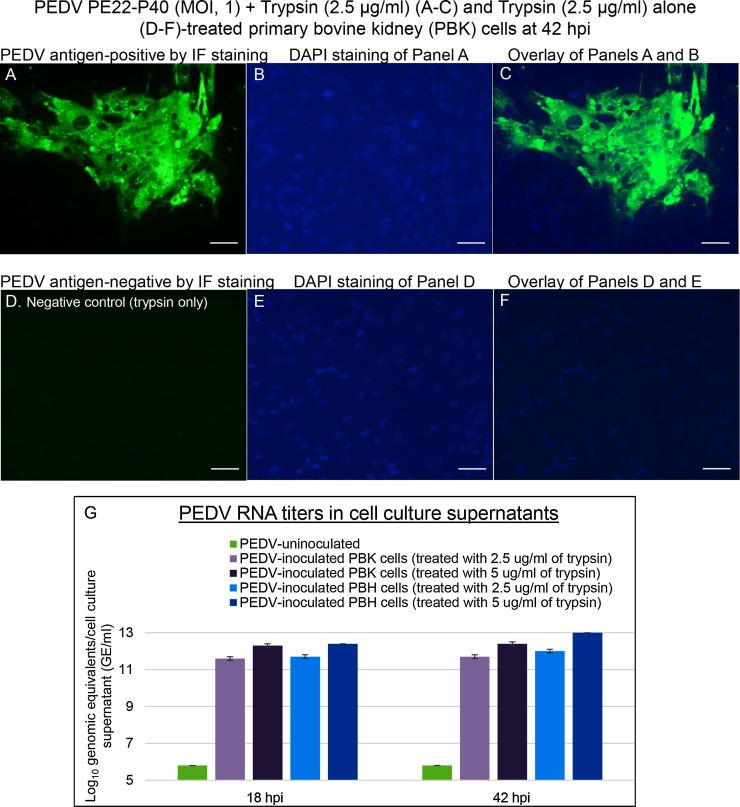
Fig. 3.
Localization of PEDV antigens by immunofluorescent (IF) staining in primary bovine kidney (PBK) cells inoculated with the PEDV strain PE22-P40 (MOI, 1), and supplemented with 2.5 μg/mL of trypsin in the cell culture medium. (A) IF staining of the inoculated PBK cells at 42 h post-inoculation (hpi), showing that the enlarged, rounded, and clustered cells are positive for PEDV antigen (green staining). (B) Blue-fluorescent 4′, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI) staining of Panel A to counterstain nuclear DNA. (C) Overlay of Panels A and B. Note that the entire clustered cells positive for PEDV antigen (arrowheads) appeared to be syncytial or multinucleated cells. (D) IF staining of PEDV-uninoculated PBK cells treated with 2.5 μg/mL of trypsin at 42 hpi, showing no cells positive for PEDV antigen. (E) DAPI staining of Panel D. (F) Overlay of Panels D and E. Scale bars =50 μm (A–F). (G) PEDV RNA titers by qRT-PCR in cell culture supernatants of PEDV-inoculated PBK and primary bovine heart cells supplemented with 2.5–5 μg/mL of trypsin at 18 and 42 hpi. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article).