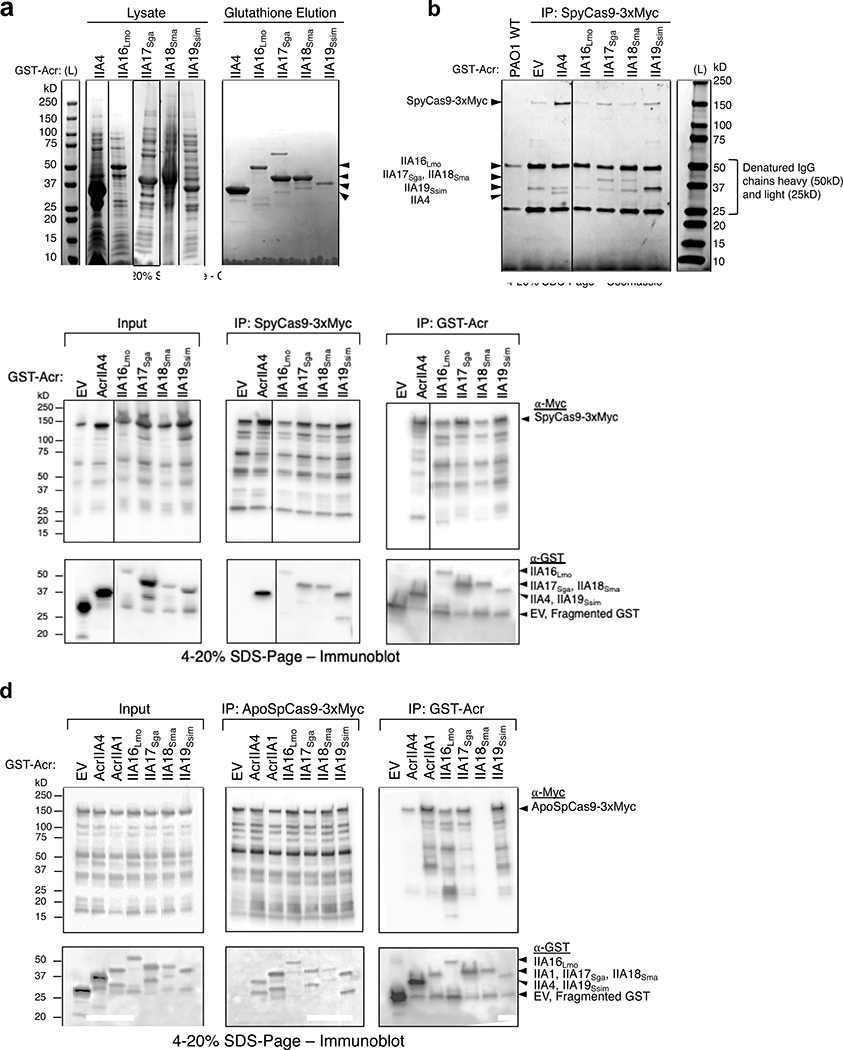
Extended Data Fig. 4. AcrIIA16–19 biochemical analysis, related to Figs 3 and 4.
a, Coomassie-stained polyacrylamide gel showing GST-tagged AcrIIA proteins (IIA4 37kD, IIA16Lmo 50kD, IIA17Sga 39kD, IIA18Sma 48kD and IIA19Ssim 42kD) purified from E. coli by elution from Glutathione Sepharose columns. Visible bands at different sizes are co-purifying proteins from E. coli. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments. b, Coomassie-stained polyacrylamide gel showing co-immunoprecipitation of Acr proteins with Myc-tagged sgRNA-bound SpyCas9 pulled down from P. aeruginosa. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments. c, d, Uncropped versions of both Myc and GST pulldowns from Figs 4a and c, displaying all fragments of (c) sgRNA-bound SpyCas9, or (d) Apo- SpyCas9 without sgRNA present. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments.