Figure 5. Platforms for tissue formation and maturation.
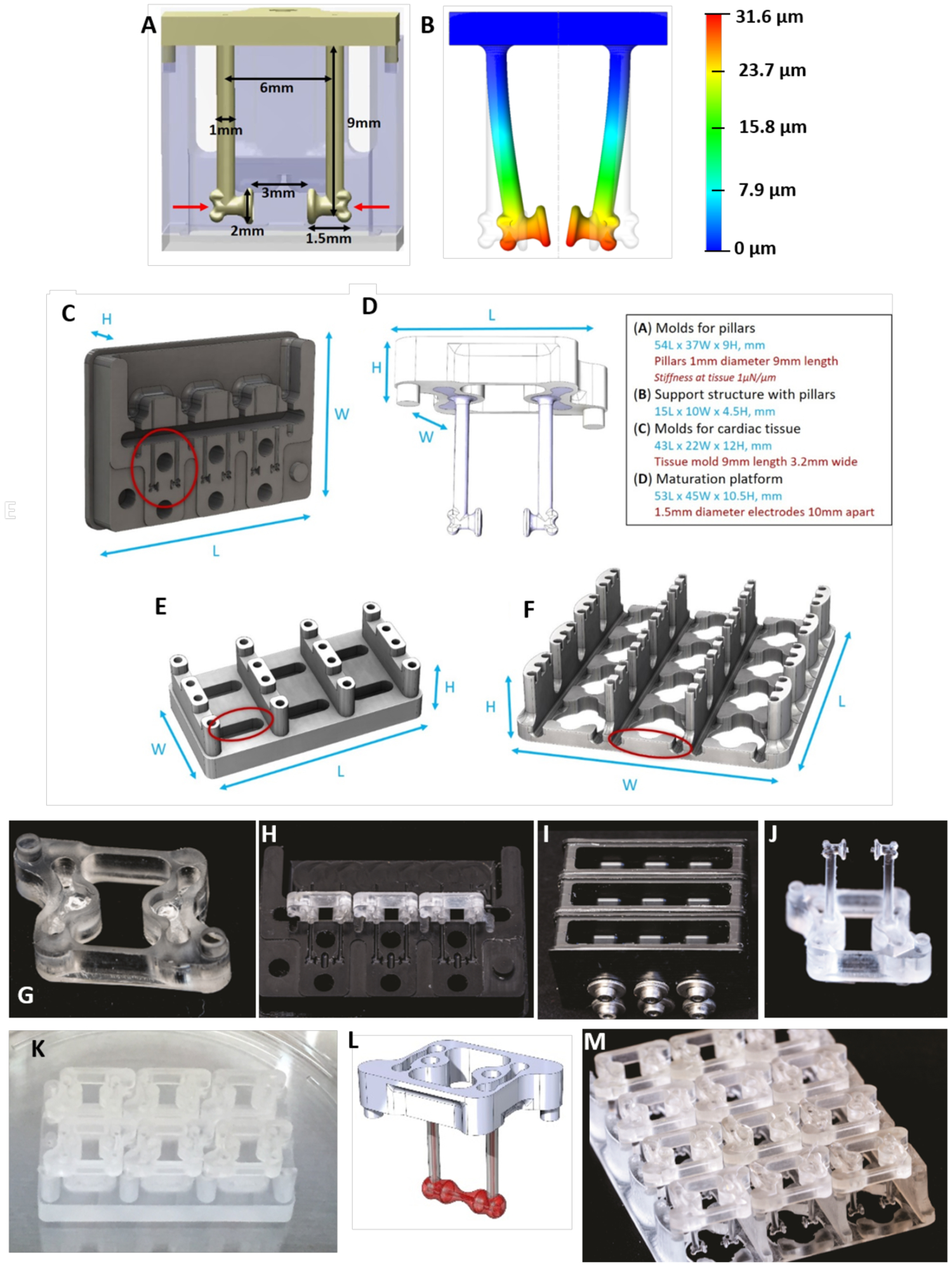
A) Dimensions of pillars and detail of a notch on the pillar’s head (indicated by red arrows). B) The design of the pillars herein enables a consistent modeling of the PDMS deflection at a set height on the pillar (i.e. where the notch is located) to facilitate on-line force readouts based on pillar deflection. C) Delrin molds for PDMS casting of pillars. D) Support structure for the pillars. E) Tissue formation platform. F) Maturation platform. G) Polycarbonate support structure for pillars with mating features. H) Three polycarbonate support structure can fit within one mold. I) Three delrin molds, containing three polycarbonate support structure each, are filled with PDMS in the top chamber and screwed tightly shut to prevent flashing. J) The polycarbonate support structure containing the cured PDMS pillars after removal from the delrin mold. K) Six polycarbonate sets of pillars with pillars can fit on one cardiac tissue formation platform. L) The polycarbonate support structure and PDMS pillars contain mating features for proper alignment in the cardiac tissue formation and maturation platforms. M) Twelve polycarbonate sets of pillars with pillars can fit on one cardiac maturation platform.
