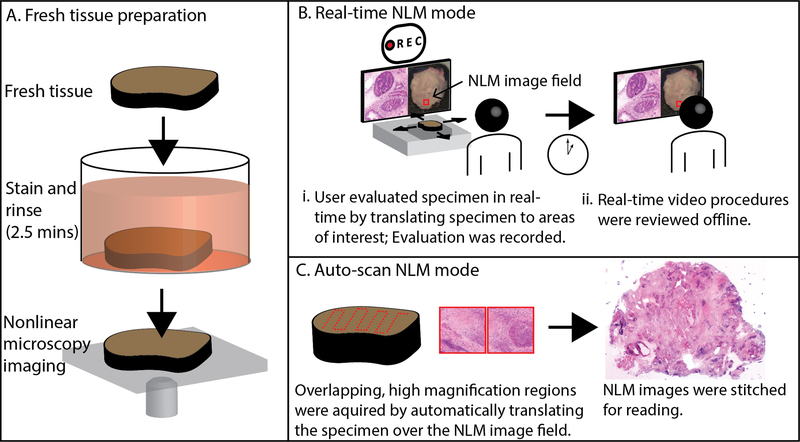
Fig. 1.
Method for evaluating fresh prostate tissue using nonlinear microscopy (NLM). A. Fresh tissue was stained in acridine orange and sulforhodamine 101 for 2 minutes, then rinsed in saline for 30 seconds. The specimen was placed on a glass specimen holder and transferred to the nonlinear microscope. The nonlinear microscope was operated in two modes: real-time nonlinear microscopy mode and auto-scan nonlinear microscopy mode. B. Real-time nonlinear microscopy mode: A white-light photograph of the specimen surface was displayed with a fiducial marker (in red) indicating the current nonlinear microscopy imaging field, providing a navigational guide. B(i) Pathologists examined the specimens on a computer monitor showing nonlinear microscopy images in an H&E color scale at 16 frames/second while translating the specimen to select the nonlinear microscopy field of view. The nonlinear microscopy evaluation procedure was recorded for offline, post-procedural review (B(ii)). C. Auto-scan nonlinear microscopy mode: a nonlinear microscopy image of the entire specimen cross section was generated by automatically acquiring a series of overlapping, high magnification regions and stitching them together.