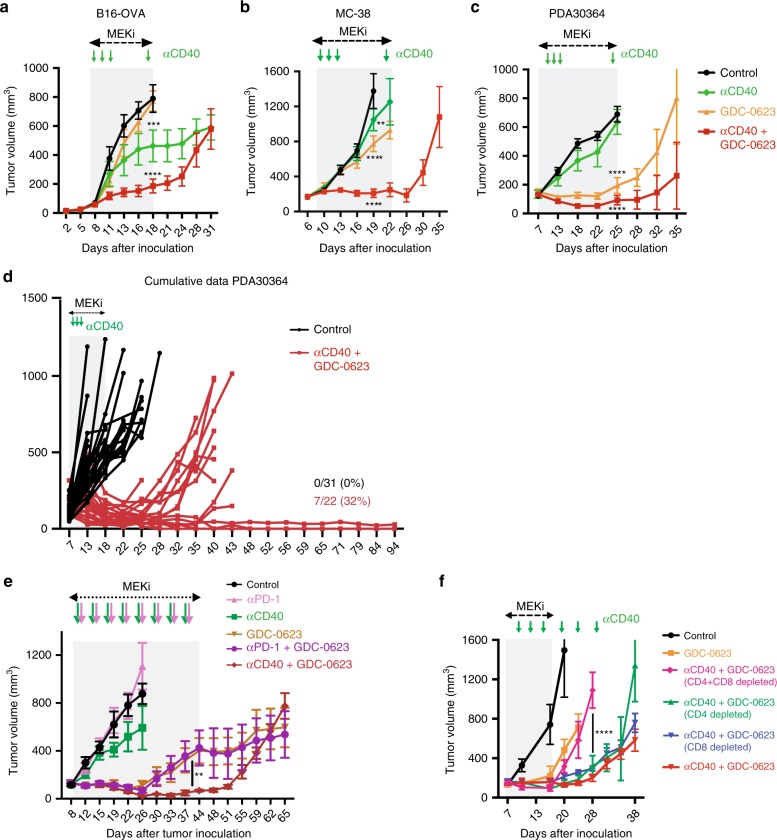
Fig. 3. Combination of MEK inhibition with agonist anti-CD40 Ab mediates control of established tumors.
a–c Outgrowth of B16-OVA, MC-38, and PDA30364 tumors upon treatment with MEKi GDC-0623 and/or anti-CD40 Ab. Mice were treated daily with 30 mg kg−1 GDC-0623 or vehicle for ~2 weeks (gray rectangle). Anti-CD40 or control Ab were administered on treatment days 3, 5, 7 as well as 1 day prior to biomarker analyses (green arrows). Each group consisted of at least six mice (nB16-OVA = 10, nMC38 = 10, nPDA30364 = 10). Four mice per group were killed at end of treatment for biomarker analyses. Two-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett’s test; treatment groups vs. control. Significance levels are indicated by asterisks (*p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001; ****p ≤ 0.0001). d Cumulative data of several experiments with the PDA30364 tumor model. e PDA30364 tumor growth in mice treated with monotherapies (anti-CD40 Ab, anti-PD-1 Ab, or GDC-0623) and combination therapies (anti-CD40 Ab + GDC-0623 and anti-PD-1 Ab+GDC-0623). Mice were treated daily with 30 mg kg−1 GDC-0623 or vehicle for ~5 weeks. Anti-CD40, anti-PD-1, and control Ab were administered twice weekly (arrows). Each group consisted of at least nine mice (nControl = 9, nCD40 = 9, nGDC-0623 = 12, nCD40+GDC-0623 = 10, nPD-1 = 10, nPD1-GDC-0623 = 11). Four mice per group were killed 2 weeks after treatment start for biomarker analyses. f Impact of T cell depletion on efficacy of GDC-0623 and/or anti-CD40 Ab treatment against PDA30364 tumors. Where indicated, groups received depletory anti-CD4, anti-CD8 or anti-CD4+ anti-CD8 Abs twice per week. Each group consisted of at least five mice.