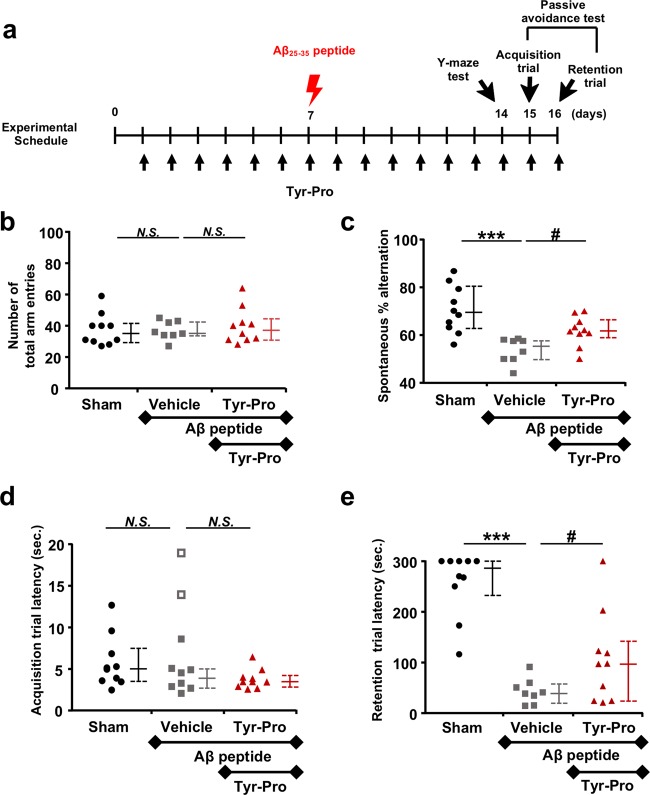
Fig. 1. Effects of oral administration of Tyr-Pro (100 mg/kg, p.o.) for 16 days on Aβ25-35-induced impairment of working and long-term memories in Y-maze test and passive avoidance test, respectively.
Tyr-Pro (100 mg/kg) was orally administered twice a day for 16 days, except for days of i.c.v. injection of Aβ25–35 peptide and the behavioural tests (Tyr-Pro administration once a day) (a). The mice received Aβ25–35 peptide injection (6 nmol/mouse, i.c.v.) on the 7th day and Tyr-Pro administration was performed after recovery from anaesthesia. The Y-maze test was started at 60 min after Tyr-Pro administration on the 14th day. The number of total arm entries (b) and percentage of spontaneous alternations (c) were evaluated. Acquisition trial on the 15th day (d) and the retention trial on the 16th day (e) were performed in the passive avoidance test. Both trials were started at 60 min after Tyr-Pro administration. Data for corresponding mice in sham (n = 10), vehicle (n = 8) and Tyr-Pro (n = 10) are depicted as closed circle, square and triangle, respectively. Two data points corresponding to mice out of normal distribution in the control group [shown as open square in (d)] were eliminated as per the interquartile outlier test. Details of the test are described in supplemental information. Data are shown as median (solid bar), and first and third quartiles (dotted lines). Statistical significance was determined by Fisher’s PLSD test and Mann–Whitney U test for Y-maze test and passive avoidance test, respectively. ***p < 0.001 vs. sham control and #p < 0.05 vs. Aβ25-35 alone. N.S. indicates no significance.