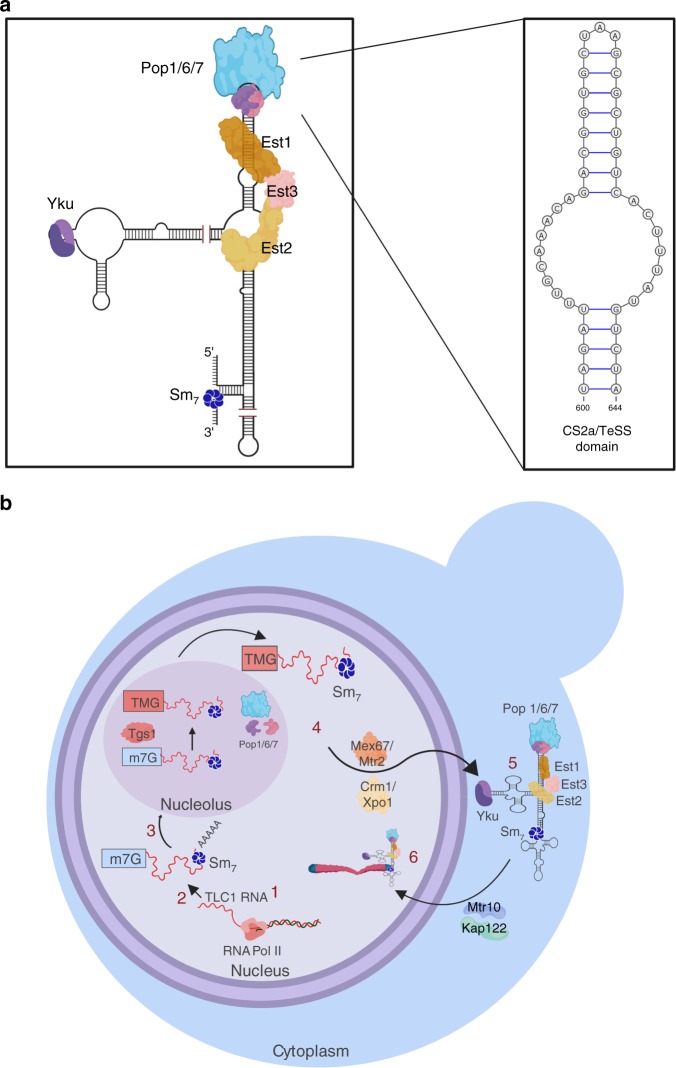
Fig. 1. Structure and biogenesis of TLC1.
a Est1 and Pop proteins bind at separable sites near the end of the Est1 arm of TLC1. Est3 interacts directly with Est1 and Est2, possibly bridging the two, and both of these associations are required for Est3 to bind telomeres. Est2 binds the central core of TLC1. (The proteins and RNA are not drawn to scale; 1a is a static representation meant to illustrate the sites on TLC1 to which the indicated proteins bind and the protein-protein interactions amongst the telomerase subunits.) The binding sites for the heterodimeric Ku complex and the Sm7 complex are also shown. Insert shows magnified view of the CS2a/TeSS domain to which a Pop6/7 heterodimer binds and then recruits Pop122. b Biogenesis of TLC1: (1) TLC1 is transcribed in the nucleus by RNA polymerase II. (2) The newly transcribed TLC1 has a 5′-7 methylguanosine cap, is bound by the Sm7 complex which helps stabilize the RNA11 and a fraction of molecules have a poly(A) 3′tail. (3) TLC1 transits to the nucleolus where the 5′ cap gets hypermethylated by the Tgs1 methyltransferase. (4) TLC1 is bound by the indicated export factors that bring it to the cytoplasm. (5) TLC1 lacking a poly(A) tail assembles with the Est proteins in the cytoplasm. (6) In G1 phase, when Est1 abundance is low, Est1 and Est3 are not TLC1-associated. However, a Yku-TLC1-Est2 complex forms and is telomere associated in G1 phase. In late S/G2 phase, the holoenzyme forms in the cytoplasm and binds import factors Mtr10/Kap122 that mediate holoenzyme entry into the nucleus. The holoenzyme binds and elongates telomeres. Pop proteins are present in the nucleoplasm, nucleolus, and cytoplasm. The compartment in which Pop proteins bind TLC1 is not known. However, Pop proteins are TLC1-associated in both G1 and G2/M phase (see text for references). Images were made in BioRender (biorender.com).