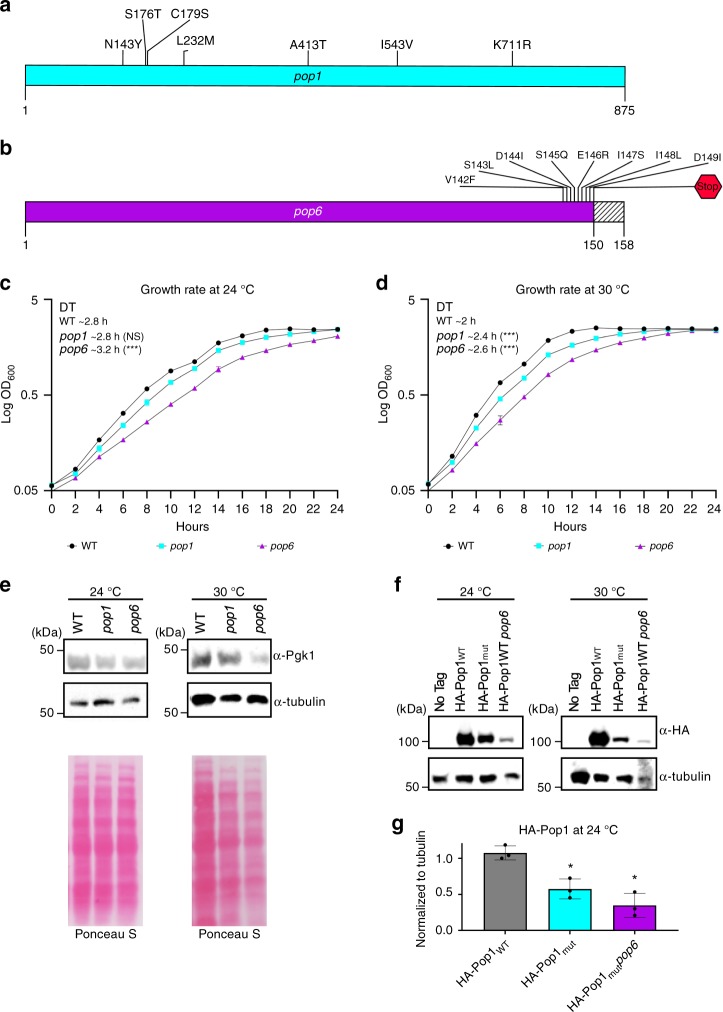
Fig. 2. Growth and global protein levels are similar in pop and WT cells at 24 °C.
Diagrams of the proteins encoded by the pop alleles used herein. Silent mutations are not shown. a The positions of the seven amino acid substitutions in the 875 amino acid protein encoded by the pop1 allele (blue) are shown. The nucleotide mutations that led to these substitutions are: 225 G → A, 427 A → T, 526 T → A, 535 T → A, 695 A → T, 792 T → C, 1237 G → A, 1627 A → G, 2132 A → G (numbers are positions of altered nucleotides). b Diagram of the protein produced by the pop6 allele (purple), which contains a deletion at nucleotide 421 resulting in an eight amino acid substitution (amino acids 142–149) and loss of the nine terminal aminoacids (dashed lines from 150–158) due to a stop codon at position 150. Growth rates of pop1 and pop6 cells at c 24 °C and d 30 °C. e Pgk1 and tubulin proteins from WT, pop1 or pop6 cells grown for ~50 generations were analyzed by western blotting. Although in this western, there appears to be more Pgk1 in WT than in pop cells at 24 °C, using a two-tailed Student’s t-test, the differences were not significant. Total protein was stained with Ponceau S. f Western blots of proteins from a no tag control strain or WT or pop6 cells expressing HA-Pop1WT or cells expressing HA-Pop1mut. g Quantification of HA-Pop1 levels from biological triplicates (black circles) of WT (gray bar), pop1 (blue bar) and pop6 (purple bar) grown at 24 °C were normalized to tubulin and WT protein levels. (Because, epitope tagged mutant Pop6 did not support viability, the effects of temperature on Pop6 were not studied). Error bars are one standard deviation from the average value of three or more independent experiments. P-values were calculated using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test; *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001; NS, not significant, P >0.05. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.