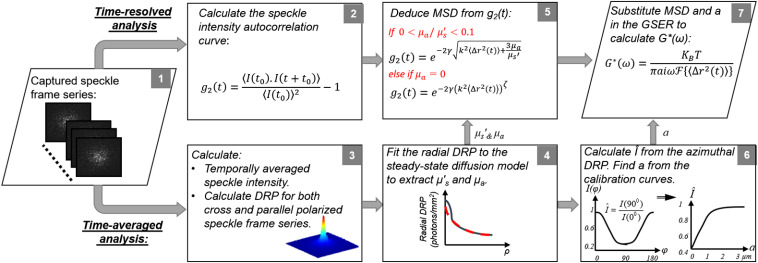
Fig. 2.
Flowchart of LSR processing algorithm (adapted with modifications from Refs. 35 and 42). Box 1: speckle images are acquired at both cross- and co-polarized states, with respect to linear polarization of the illumination beam. Box 2: cross-correlating the first speckle frame with subsequent frames provides the speckle intensity autocorrelation function, . Box 3: temporal averaging of speckle frames returns the DRP at both cross- and co-polarized states. Box 4: the and are experimentally evaluated via curve-fitting to the radial cross-polarized DRP. Box 5: optical properties determine whether the DWS formalism, i.e., or the modified MCRT-driven equation, i.e., , should be used to deduce the MSD. Box 6: the ratio of co-polarized DRP along short and long axes, i.e., , is compared with a calibration curve to evaluate the average radius of scattering particles, . Box 7: MSD and are substituted in GSER to calculate the .