Fig. 5. Activation model of OsGA2oxs and OsDAO and phylogenetic analysis.
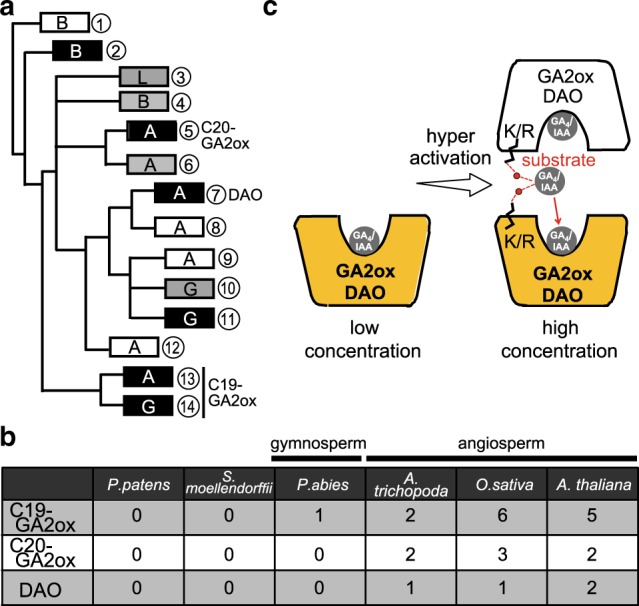
a Schematic phylogenetic tree of C19- and C20-type GA2oxs and DAOs, including some 2ODD enzymes bearing close resemblance to these enzymes. Each box corresponds to each clade with the same number presented in Supplementary Fig. 10. Clades containing only 2ODD enzymes with R/K at the 308th position of OsGA2ox3 or not are shown in black or white, whereas clades including both types are shown in gray. Bryophytes, lycophytes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms are shown as B, L, G, and A characters, respectively. b The number of gene copies of C19- and C20-type GA2ox and DAO in P. patens (Bryophytes), S. moellendorffii (Lycophytes), P. abies (Gymnosperms), A. trichopoda (the most primitive lineage of Angiosperms), O. sativa (monocot), and A. thaliana (dicot). c Under low substrate concentration (GA4 or IAA) (left), GA2ox or DAO functions as a monomer with low enzyme activity. At high substrate concentration (right), the interface GA4 or IAA causes the formation of multimers by bridging two enzyme molecules, resulting in hyperactivation.
