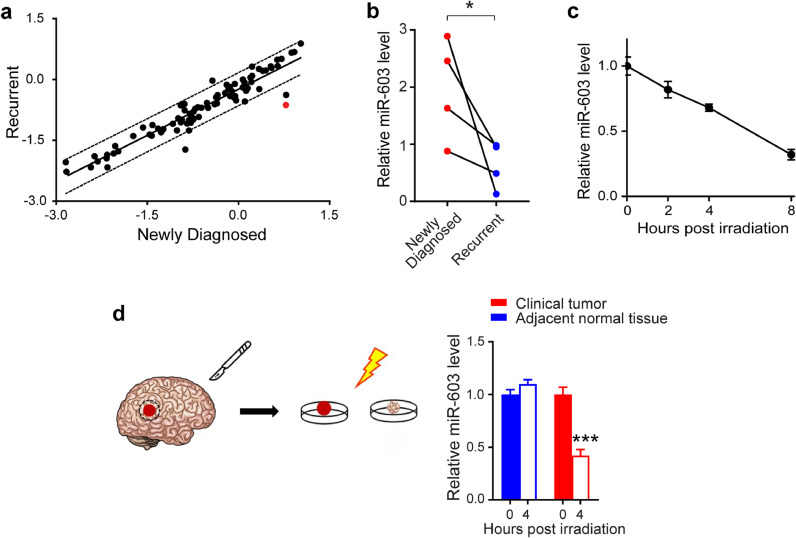
Fig. 1.
Ionizing radiation induces lower level of miR-603 in glioblastoma. (a) Scatter plot of the human miScript miRNome miRNA profiling depicted the relative expression of miRNA in the matched pre- (plotted on the x-axis) and post-treatment (plotted on the y-axis) clinical samples. All samples harbor wtIDH and umMGMT. Significant deviation from the solid 45° line indicates significant change in relative abundance after treatment. Each data point represents the average of triplicate results. Points lying outside of the dotted line indicate significant change in relative abundance. miR-603 is indicated in red. (b) Glioblastoma that recurred after IR/TMZ treatment exhibited decreased levels of miR-603. RNAs were extracted from FFPE samples obtained from the same patients (labelled as newly diagnosed and recurrent). Four matched pairs were analyzed. miR-603 levels were determined by qPCR. *p < 0.05 between newly diagnosed group and recurrent group (Student's t-test). (c) IR reduced cellular level of miR-603 in LN340 glioblastoma line. qPCR was performed to measure miR-603 levels in LN340 cells treated with 6 Gy IR at the indicated times. (d) IR reduced miR-603 level in freshly resected glioblastoma samples. miR-603 level was measured using qPCR in freshly resected human glioblastoma specimens or adjacent normal tissue after 2 Gy IR treatment. ***p < 0.001 compared to unirradiated group (Student's t-test).