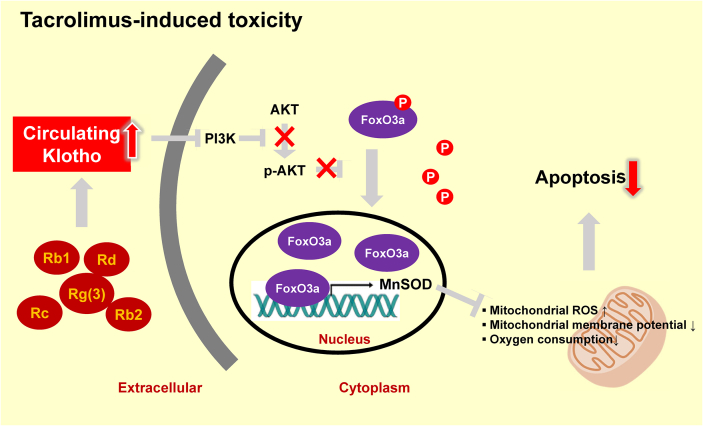
Fig. 4.
Schematic diagram summarizing the predicted mechanism whereby ginseng influences regulation of the antiaging gene Klotho. PI3K/AKT-mediated phosphorylation of FoxO3a is induced by reduced Klotho expression in response to tacrolimus treatment. Under these conditions, FoxO3a appears to be maintained in an inactive form in the cytoplasm. However, the restoration of Klotho levels in response to ginseng treatment induces the nuclear translocation of FoxO3a via the suppression of PI3K/AKT activity and an increase in the levels of MnSOD. By maintaining Klotho expression, ginseng may prevent tacrolimus-induced oxidative damage and apoptotic cell death. These findings provide evidence for the protection mechanism of ginseng via the antiaging gene Klotho against a background of oxidative stress-associated injury. FoxO3a, forkhead box O3; P, phosphorylation; MnSOD, manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase.