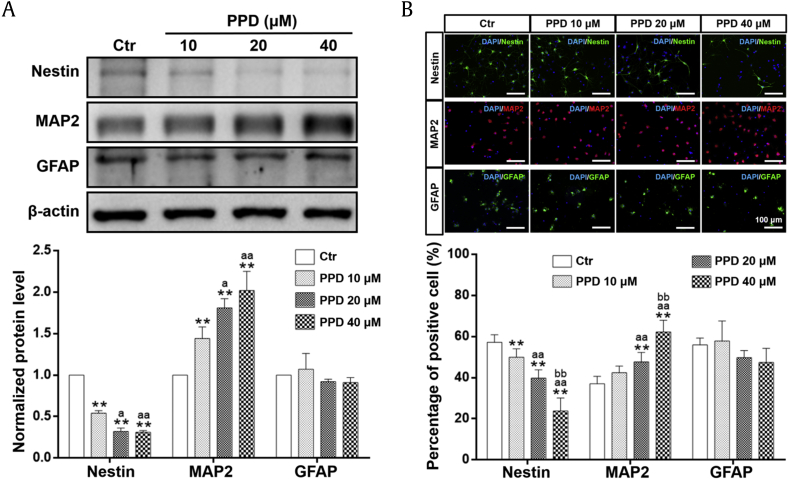
Fig. 3.
PPD selectively induces neural differentiation of NSCs. After NSCs were incubated with different concentrations of PPD for 7 days, PPD significantly promoted NSC differentiation into neurons in a dose-dependent manner monitored by Western blot analysis (A) and immunofluorescent staining (B). (A) PPD (10, 20, 40 μM) significantly downregulated the expression of nestin and upregulated the expression of MAP2, whereas the expression of GFAP showed a downward but nonsignificant trend. (B) The proportion of nestin-positive cells was significantly decreased and the proportion of MAP2-positive cells was increased by PPD treatment (10 μM, 20 μM, 40 μM). Scale bars: 100 μm. Data represent the means ± SD. **p < 0.01, compared with the Ctr group; ap < 0.05 and aap < 0.01, compared with the 10 μM PPD group; bbp < 0.01, compared with the 20 μM PPD group. PPD, 20(S)-protopanaxadiol; NSC, neural stem cell; MAP2, microtubule-associated protein 2; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; Ctr, control; SD, standard deviation.