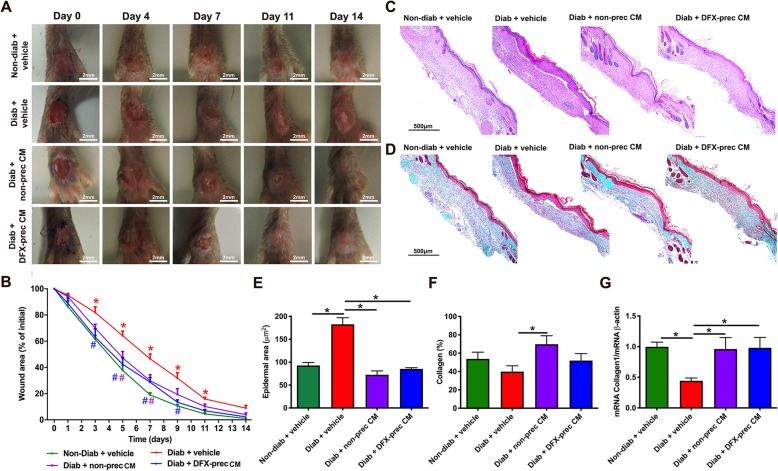
Fig. 7.
AD-MSC-conditioned medium administration accelerates wound healing in diabetic mice. a Representative digital photographs of the dorsal surface of the feet of 26-week-old non-diabetic and diabetic mice treated with vehicle, conditioned medium derived from non-preconditioned AD-MSCs, or conditioned medium derived from DFX-preconditioned AD-MSCs at different days after wound induction. b Quantification of kinetics of wound closure. Wound size for each day was defined as the area that was not re-epithelized and was normalized by the initial wound area. c Representative bright-field images of hematoxylin and eosin-stained histological sections of the wounds, 14 days after wound induction, for evaluation of epidermal area. d Representative bright-field images of Masson’s trichrome stained histological sections of the wounds, 14 days after wound induction for evaluation of collagen deposition. e Quantification of epidermal area in the wound bed. f Quantification of collagen deposition in the wound bed. g Quantification of mRNA levels of type I collagen in the wound bed 7 days after wound induction. Data were normalized against the housekeeping gene β-actin. Quantitative data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. (n = 6, one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test, *p < 0.05)