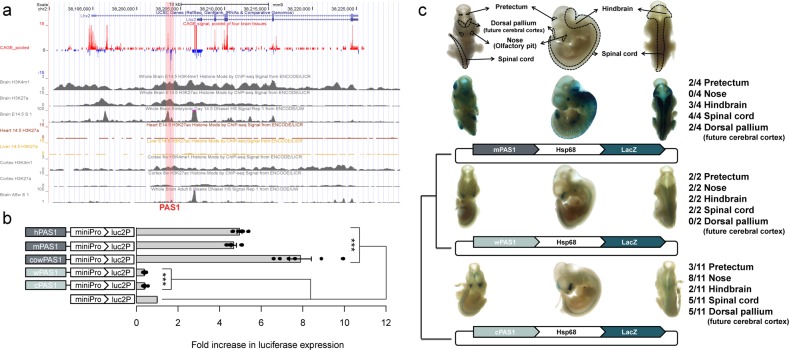
Fig. 2. Effects of PAS1s from various amniotes on reporter gene expression in mouse neuroblastoma cell line (Neuro2A) and embryonic nervous system.
a Epigenomic signals on PAS1 (pink box). The CAGE signals pooled from four mouse brain samples showed peaks in both sense (red) and antisense (blue) strands of PAS1. The data were obtained from FANTOM (http://fantom.gsc.riken.jp/).78,79 H3K4me1 and H3K27ac signals on PAS1 were seen in mouse embryonic brain samples, but not in embryonic heart and liver samples. All H3K4me1, H3K27ac, and DNase I hypersensitive signals on PAS1 in E14.5 mouse brain samples were higher than those in adult (8 weeks) mouse brain samples. b Cis-regulatory activity of PAS1s from various amniotes on reporter gene expression. The PAS1 elements from placental mammals, e.g., human (hPAS1), mouse (mPAS1) and cow (cowPAS1), enhanced, but those from wallaby (wPAS1) and chicken (cPAS1) suppressed the expression of the luciferase reporter gene (luc2P) in Neuro2A cells. The expression levels of the luciferase gene linked to PAS1 were normalized to those of the same gene driven by the minimal promoter (miniPro) without PAS1. Error bars represent the SEM of six biological replicates with three technical replicates for each experiment. One-tailed Student’s t-test, ***P < 0.001. c Effect of PAS1s from various amniotes on the expression of LacZ reporter gene in E11.5 mouse embryos. Locations of pretectum, dorsal pallium, primitive nose, primitive hindbrain, and spinal cord in ventral, lateral, and dorsal views are indicated. The denominator of the fraction on the right indicates the total number of LacZ-positive embryos obtained (Supplementary information, Fig. S2), and the numerator denotes the number of embryos with reproducible LacZ expression in a specific region of the embryo (Supplementary information, Fig. S2). Hsp68, a minimal promoter; LacZ, β-galactosidase gene.