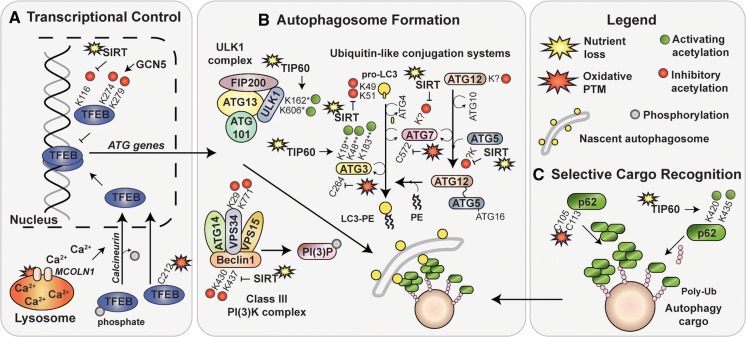
Fig. 2.
Autophagy targets of acetylation and oxidation. Nutrient and oxidative stresses affect proteins that participate in autophagy by lysine (K) acetylation or cysteine (C) oxidation. a Localization of transcriptional factor EB (TFEB), a master regulator of autophagy and lysosomal gene expression, is regulated by oxidative stress. Indirectly, oxidative modification of mucolipin 1 (MCOLN1) leads to TFEB dephosphorylation by Ca2+-sensitive phosphatase, calcineurin and its translocation to the nucleus. Directly, oxidation of TFEBs redox-sensitive residue, C212, promotes rapid nuclear localization. In addition, inhibitory lysine acetylation of K274 and K279 that is regulated by the general control non-repressed protein 5 (GCN5) prevents TFEB dimerization. The molecular and functional outcomes of K116 are not known, but are opposed by nutrient sensitive, NAD + -dependent lysine deacetylase (KDAC), SIRT1. b Acetylation-sensitive lysine residues were detected within members of the ULK1 complex, the class III PI(3)K complex and both ubiquitin-like conjugation systems. Unc-51-like kinase 1 (ULK1, ULK1 complex) contains two lysine residues, K162 and K606 (* in mouse) that are acetylated by TIP60 in response to serum starvation. Vacuolar protein sorting 34 (VPS34, class III PI(3)K complex) contains two acetylation sensitive lysine residues (K29 and K771) that are subject to inhibitory acetylation in fed conditions. Inhibitory acetylation of residues K430 and K437 in Beclin 1 (class III PI(3)K complex) is opposed by nutrient-sensitive SIRT1 KDAC. Within the ubiquitin-like conjugation systems, LC3 (K49, K51), ATG5 (unknown), ATG7 (unknown) and ATG12 (unknown) are subject to inhibitory acetylation by p300 (not shown) in fed conditions. Acetylation of LC3, ATG5 and ATG7 residues is opposed by SIRT1 deacetylase. ATG3 is subject to activating acetylation by TIP60 in starved conditions. Acetylation of lysine residues K19, K48 and K183 (** in yeast) is necessary for ATG3 enzymatic activity and LC3 binding affinity. ATG3 and ATG7 are also subject to inactivation by oxidative stress due to oxidation of their catalytic thiols, C264 and C572, respectively. c Selective autophagy receptor p62 is a target of both, acetylation and oxidation. TIP60-dependent activating acetylation of K420 and K435 residues within the ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domain prevent UBA dimerization and enhance ubiquitin (Ub) binding affinity. Oxidation of C105 and C113 promotes p62 oligomerization and stimulates autophagy by intermolecular disulphide bond formation