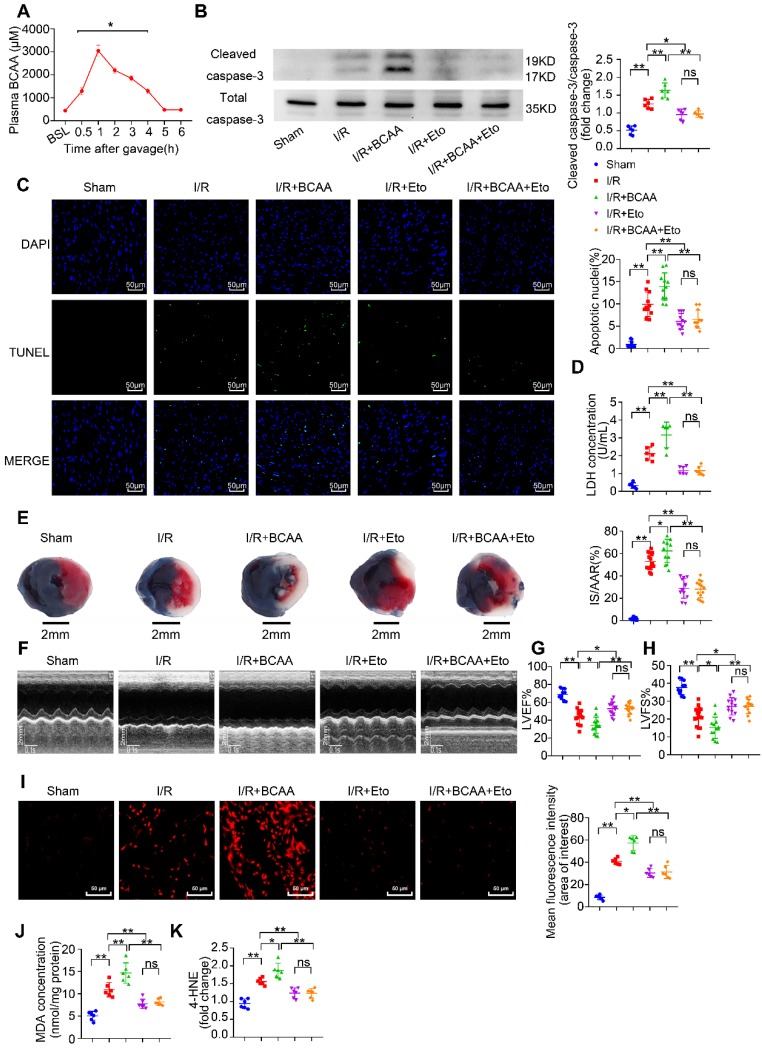
Figure 3.
BCAA worsen I/R injury, which can be rescued by inhibiting FAO. (A) Serum BCAA concentrations at different time points after gavage (weight ratio, leucine: valine: isoleucine=2:1:1, 1.5 mg/g/day, n=6-8). (B-K) Vehicle or BCAA-supplemented (1.5 mg/g/day, 7 days) mice were treated with or without Eto (20 mg/kg body weight, i.p. injection 15 min before I/R surgery) under basal or I/R conditions. (B) Cardiac cleaved and non-cleaved caspase-3 by western blotting (n=6). (C) Representative cardiac apoptosis determined by TUNEL staining. Green fluorescence indicated TUNEL-positive cardiomyocyte nuclei; blue fluorescence showed total cardiomyocytes nuclei (n=10-15). Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) Cardiac apoptosis by LDH release assay (n=6). (E) Infarct area of heart tissue by Evans blue and tetrazolium chloride (TTC). The blue area represented unaffected heart tissue; white area showed infarcted tissue; red pus white area indicated tissue at risk (n=10-15). Scale bar: 2 mm. (F) Representative M-Mode echocardiographic images. (G and H) Echocardiographic assessment of LV ejection fraction and LV fractional shortening (n=10-15). (I) Superoxide production detected by DHE staining (n=6). Scale bar: 50 μm. (J and K) Lipid peroxidation determined by MDA and 4-HNE contents (n=6). (A) Data were analyzed by Student's t test. (B-K) Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, followed by a Bonferroni post-hoc test. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01. All values are presented as mean ± SEM.