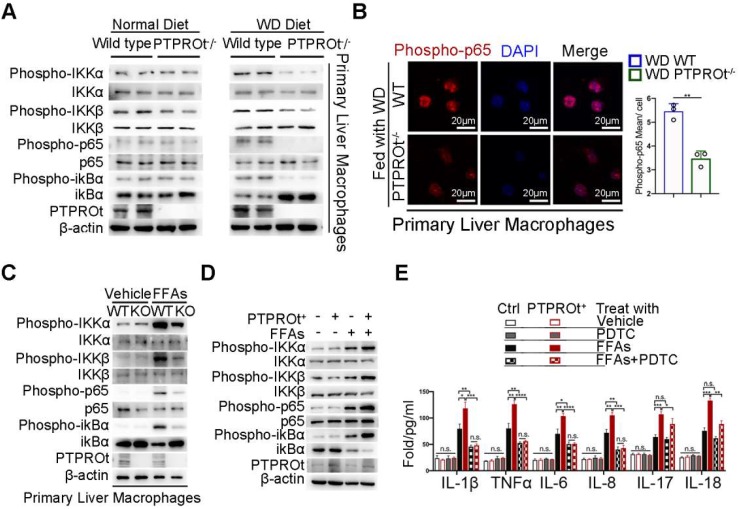
Figure 2.
PTPROt deficiency in liver macrophages causes decreased activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. A. Immunoblotting of phospho-IKKα, IKKα, phospho-IKKβ, IKKβ, phospho-P65, P65, phospho-ikBα, ikBα, PTPROt, and β-actin (loading control) in primary WT and PTPROt-/- liver macrophages that were isolated from the mice described in Figure 1A. B. Fluorescence microscopy of phospho-p65 in primary WT and PTPROt-/- liver macrophages isolated from the mice described in Figure 1A. DAPI, DNA-binding dye. Bar = 20 μm. Quantification of phospho-P65 per cell was shown. C. Immunoblotting of phospho-IKKα, IKKα, phospho-IKKβ, IKKβ, phospho-P65, P65, phospho-ikBα, ikBα, PTPROt, and β-actin (loading control) in primary liver macrophages isolated from WT and PTPROt-/- mice treated with vehicle and free fatty acids (FFAs) for 24 hr. D. Immunoblotting of phospho-IKKα, IKKα, phospho-IKKβ, IKKβ, phospho-P65, P65, phospho-ikBα, ikBα, PTPROt, and β-actin (loading control) in RAW-ctrl and RAW-PTPROt+ cells treated with/without FFAs for 24 hr. E. The levels of IL-1β, TNFα, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17, and IL-18 in cell culture supernatants from RAW-ctrl and RAW-PTPROt+ cells treated with or without FFAs and/or PDTC for 24 hr were detected by ELISA. Abbreviations: DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; FFAs: Free Fatty Acids; KO: the primary liver macrophages isolated from PTPROt knockout mice; PDTC: Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate; WT: the primary liver macrophages isolated from wild-type mice.