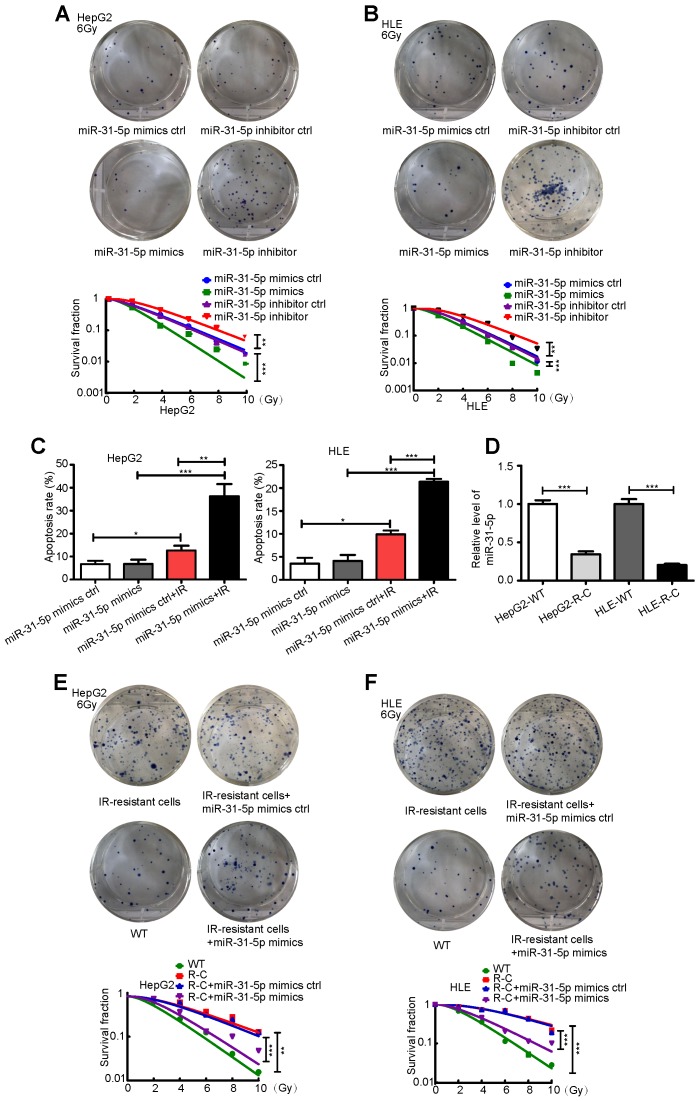
Figure 2.
miR-31-5p sensitized HCC to radiation in vitro. (A-B) Radiation sensitivity was tested with colony formation assays in both cell lines with different levels of miR-31-5p. In both cell lines, miR-31-5p downregulation increased colony formation upon exposure to 6 Gy irradiation, and miR-31-5p upregulation decreased colony formation upon exposure to 6 Gy irradiation. Top: Representative images of colony formation assays. Bottom: Statistical analysis results (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (C) The apoptosis rate of HepG2 and HLE cells with different miR-31-5p levels upon irradiation was validated by flow cytometry (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (D) The levels of miR-31-5p in HepG2-R-C and HLE-R-C were validated by qRT-PCR (***P < 0.001). (E-F) Radiation sensitivity of HepG2-R-C and HLE-R-C with different levels of miR-31-5p. HepG2 R-C and HLE R-C formed more colonies upon exposure to 6 Gy radiation than HepG2 WT and HLE WT cells, and this pattern was reversed by the miR-31-5p mimics. Top: Representative images of colony formation assays. Bottom: Statistical analysis results (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). All of the above results are representative of three independent experiments. Abbreviations: ctrl, control; WT, wild-type; R-C, radiotherapy-resistant cells; IR, irradiation; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.