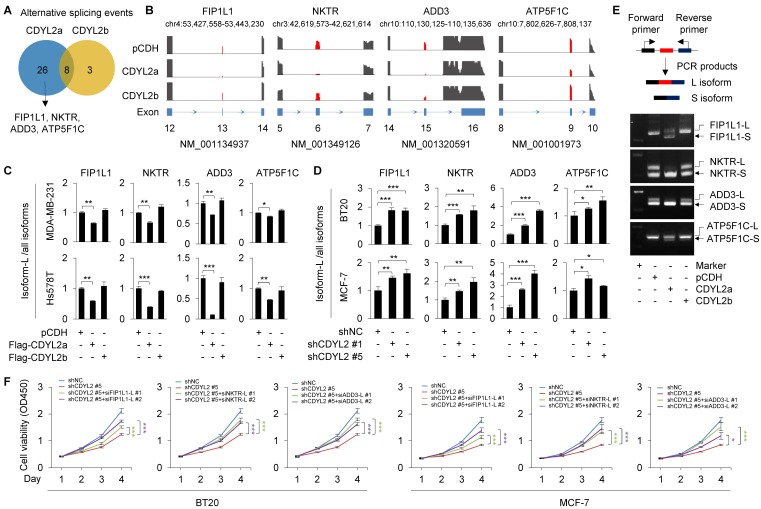
Figure 5.
CDYL2a promotes breast cancer cell proliferation through regulating alternative splicing of FIP1L1, NKTR, and ADD3 genes. (A) Hs578T cells stably expressing pCDH, Flag-CDYL2a, or Flag-CDYL2b were subjected to RNA-seq analysis and alternative splicing events with FDR < 0.05 and absolute ΔPSI value > 0.1 are shown. (B) Exon skipping events within FIP1L1, NKTR, ADD3, and ATP5F1C genes are shown. (C) qPCR analysis was conducted with isoform-specific primers using MDA-MB-231 and Hs578T cells stably expressing pCDH, Flag-CDYL2a, or Flag-CDYL2b. The ratios of the L isoforms to all isoforms of FIP1L1, NKTR, ADD3, and ATP5F1C genes are shown. (D) qPCR analysis was performed with isoform-specific primers using BT20 and MCF-7 cells stably expressing shNC, shCDYL2#1, or shCDYL2#5. The ratios of the L isoforms to all isoforms of FIP1L1, NKTR, ADD3, and ATP5F1C genes are shown. (E) RT-PCR validation of individual splicing events regulated by CDYL2a. The cDNA from Hs578T cells stably expressing pCDH, Flag-CDYL2a, or Flag-CDYL2b were subjected to PCR amplification using primers flanking the alternative exon. (F) BT20 and MCF-7 cells stably expressing shNC and shCDYL2#5 were transfected with the indicated siRNAs targeting the L isoforms of FIP1L1, NKTR, or ADD3 gene. After 48 h of transfection, cells were subjected to cell proliferation assays using CCK-8 kit. The knockdown effect of transfected siRNAs targeting the L isoforms of FIP1L1, NKTR, ADD3 genes was validated by qPCR analysis and the corresponding results are shown in Figure S14. *, **, and *** are significant differences at p<0.05, p<0.01, and p<0.001 levels, respectively.