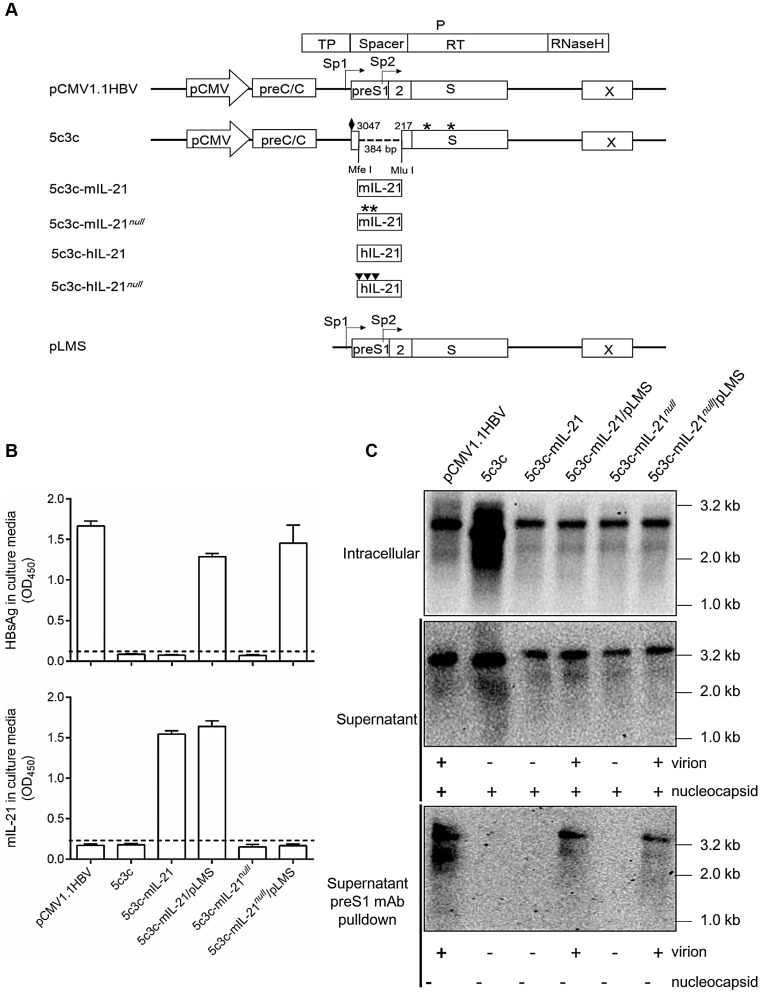
Figure 1.
Construction and characterization of 5c3c-derived rHBV expressing IL-21. (A) Schematic representation of plasmid constructs. Open boxes and arrows represent ORFs and promoters, respectively. Stop codons in the S and murine IL-21 (mIL-21) ORFs are indicated by asterisks. Solid diamonds indicate ATG to ACG mutation at preS1 start codon. Solid triangles indicate ATG to ACG mutation at 1st, 8th and 11th codons in human IL-21 (hIL-21) ORF. Restriction enzyme sites (MfeⅠ and MluⅠ) used for inserting cargo sequences and nucleotide positions on HBV genome are indicated. Murine and human IL-21 sequence modifications are detailed in Figure S2 and Figure S3. (B) Supernatants from Huh-7 transfected with indicated plasmids in triplicates were assayed for HBsAg (top) and mIL-21 (bottom) using ELISA. Group means and SEMs are presented. Dotted lines represent cut-off thresholds. (C) Southern blot analysis of intracellular capsid-associated HBV DNA (top), capsid- and virion-associated HBV DNA in the supernatants (middle), and virion-associated DNA in the supernatants captured by anti-preS1 mAb (bottom). Expected presence of HBV capsid and virions in supernatants with or without anti-preS1-capture are indicated below the blots. Transfections were independently repeated with similar results and representative data from one experiment are shown.