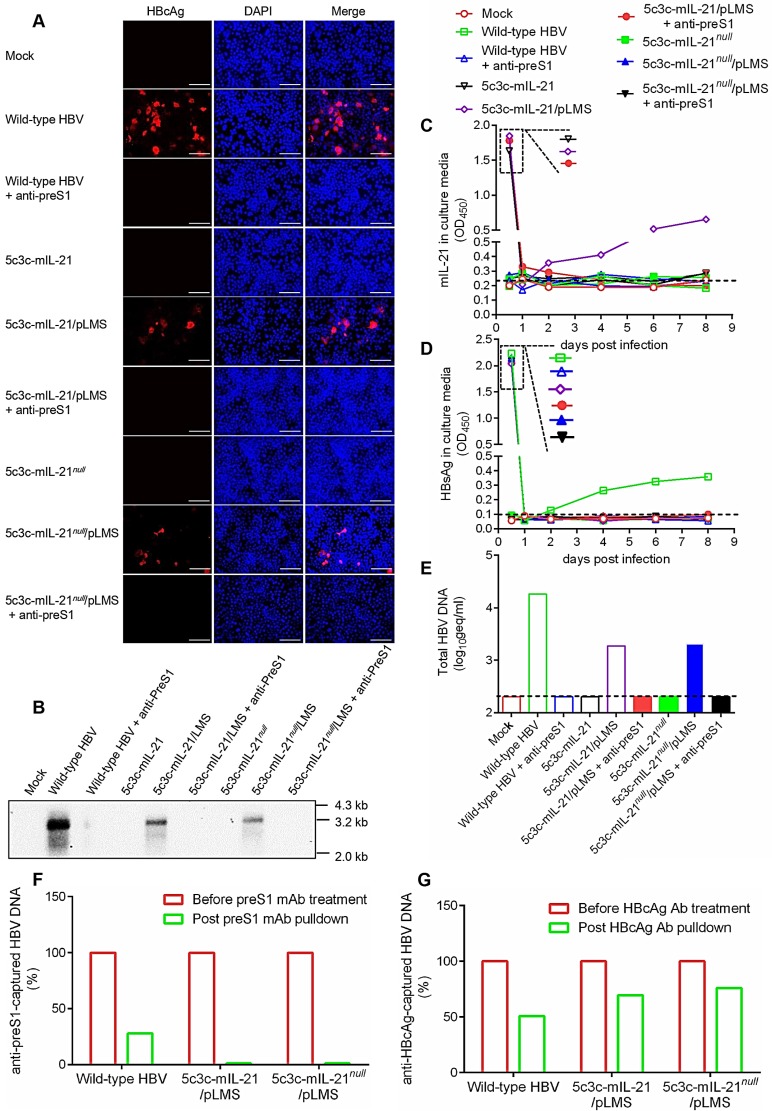
Figure 4.
Infection of HepG2/NTCP cells by mIL-21-expressing rHBV virions. Concentrated supernatants from HepAD38 cells, 5c3c-mIL-21/pLMS and 5c3c-mIL-21null/pLMS co-transfected Huh-7 cells, with or without pre-incubation with anti-preS1 mAb, were used to infect HepG2/NTCP cells. Concentrated supernatants from mock transfection was used as negative control. Concentrated supernatants from 5c3c-mIL-21 and 5c3c-mIL-21null mono-transfections, which contained only naked nucleocapsids (see Figure 1), were used to exclude the possibility of capsid-mediated transduction. Culture media were changed at day 0.5, 1 and 2 post infection, and then every 2 days. On day 8, cells were subjected to DAPI and anti-HBcAg staining and visualized using fluorescence microscopy (A), and intracellualr HBV replication was analyzed in Southern blot using HBV-specific probes (B). Scale bars, 100 μm. mIL-21 (C) and HBsAg (D) in culture media at indicated time points were measured using ELISA. (E) HBV DNA in day 8 culture media was analyzed using quantitative real time PCR. (F) HBV DNA in day 8 culture media of cells infected with indicated supernatants were analyzed using quantitative real time PCR with or without capture by anti-preS1 mAb or anti-HBcAg antibody. Captured HBV DNA levels were normalized against total HBV DNA levels without antibody pulldown. Dotted lines represent cut-off thresholds (C and D), and lower limit of quantification (E), respectively. ELISA and qrtPCR were performed in duplicates and triplicates, respectively, and mean values were used for plotting. Infections were independently repeated with similar results and representative data from one experiment are shown.